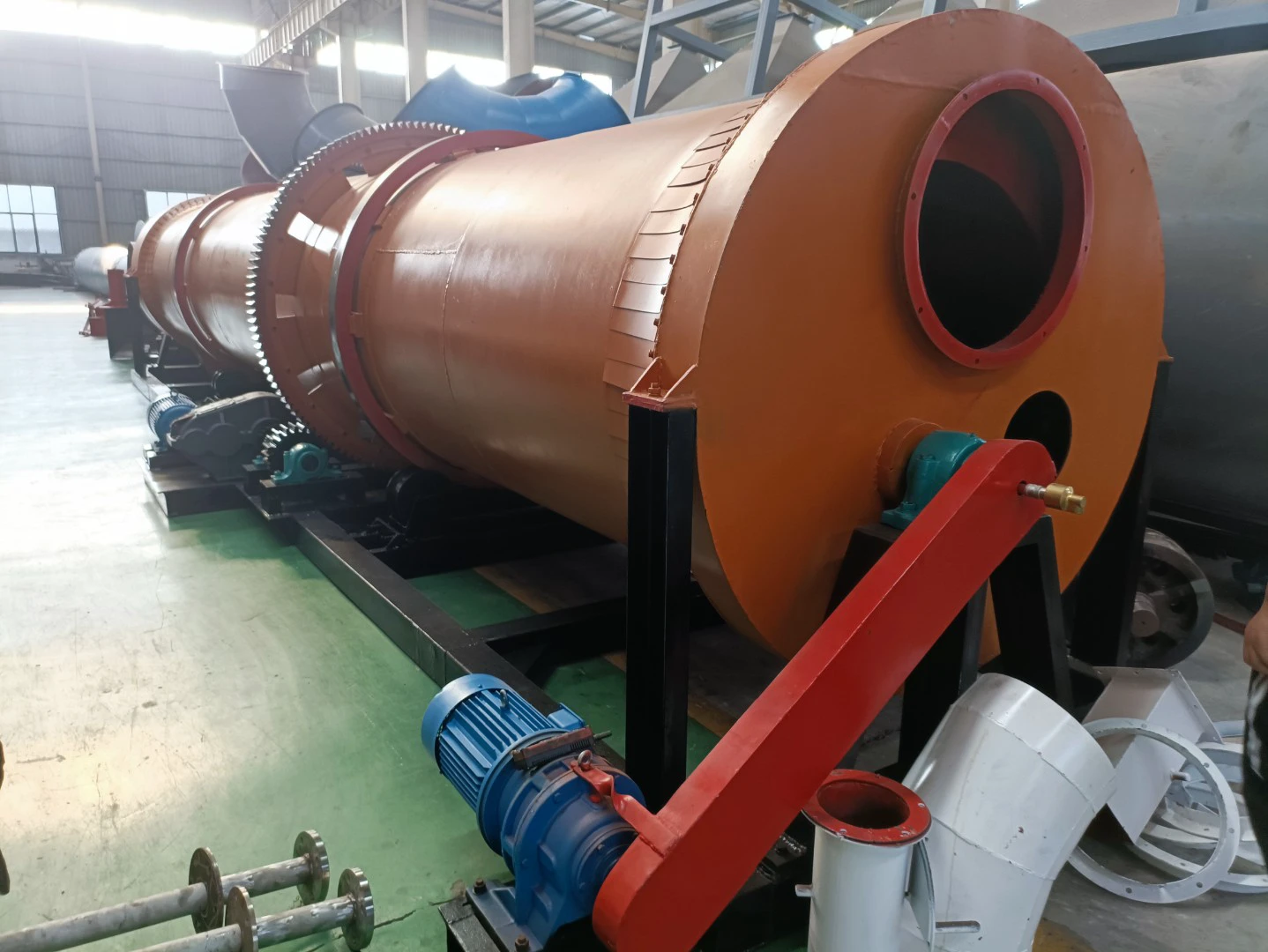
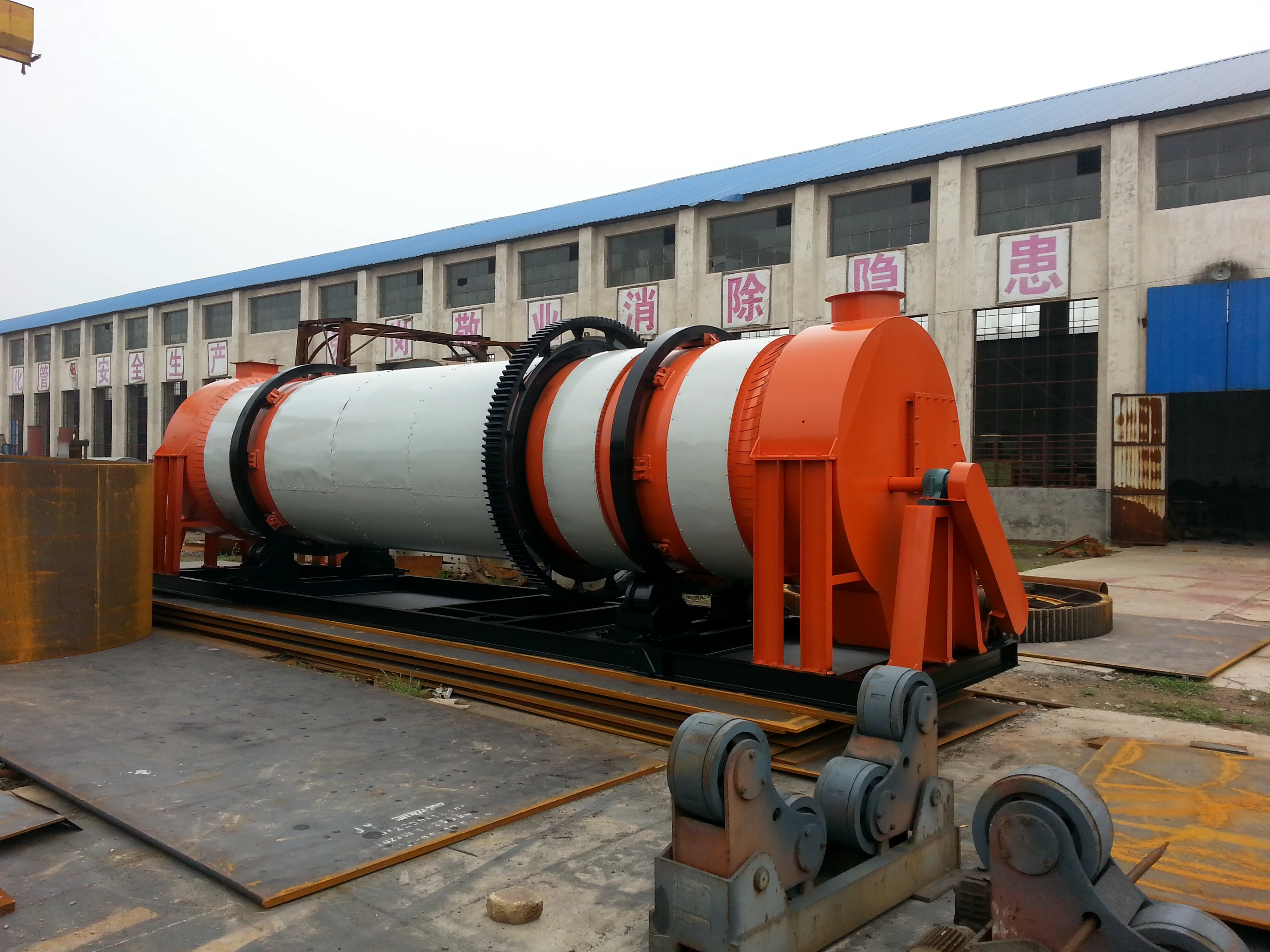
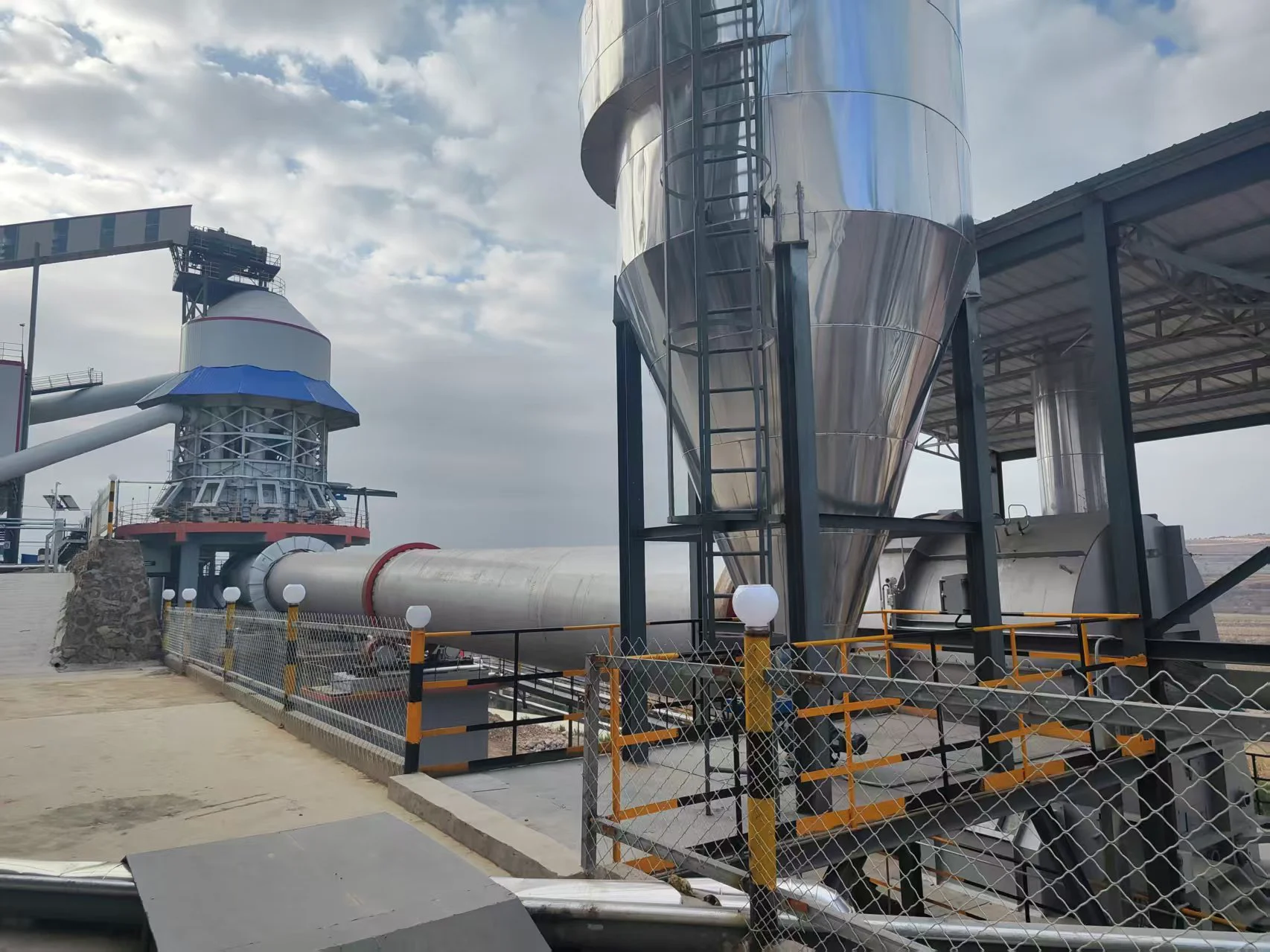
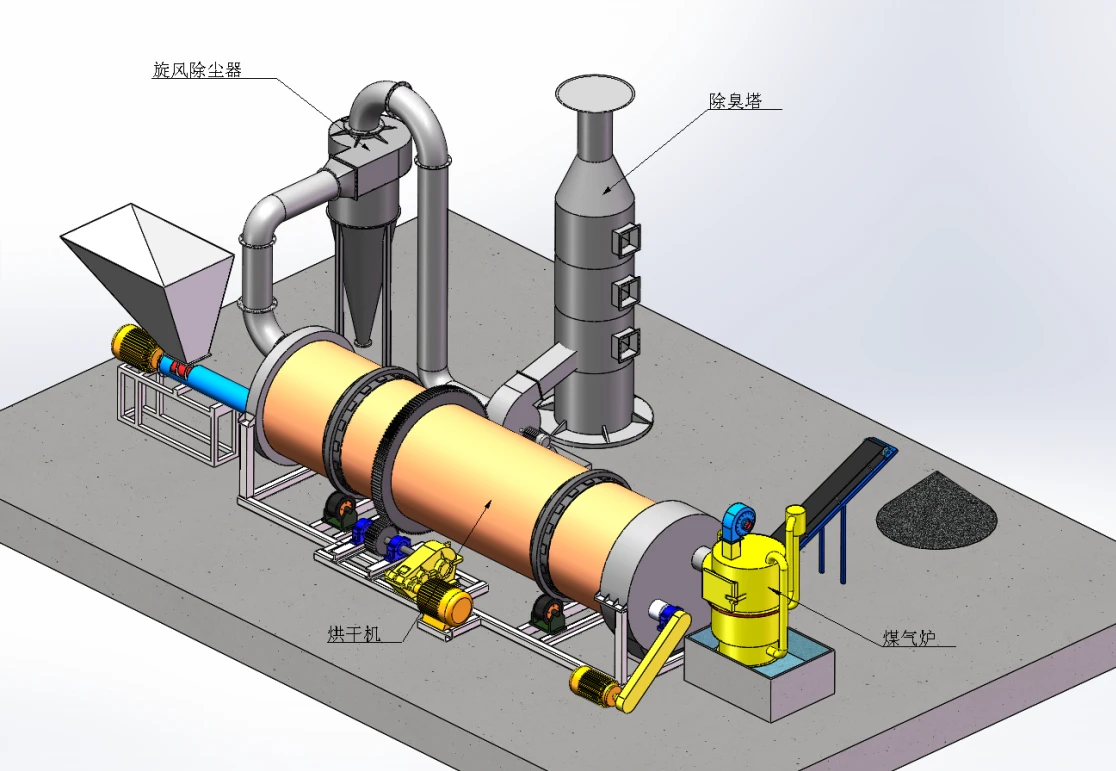
Working principle:
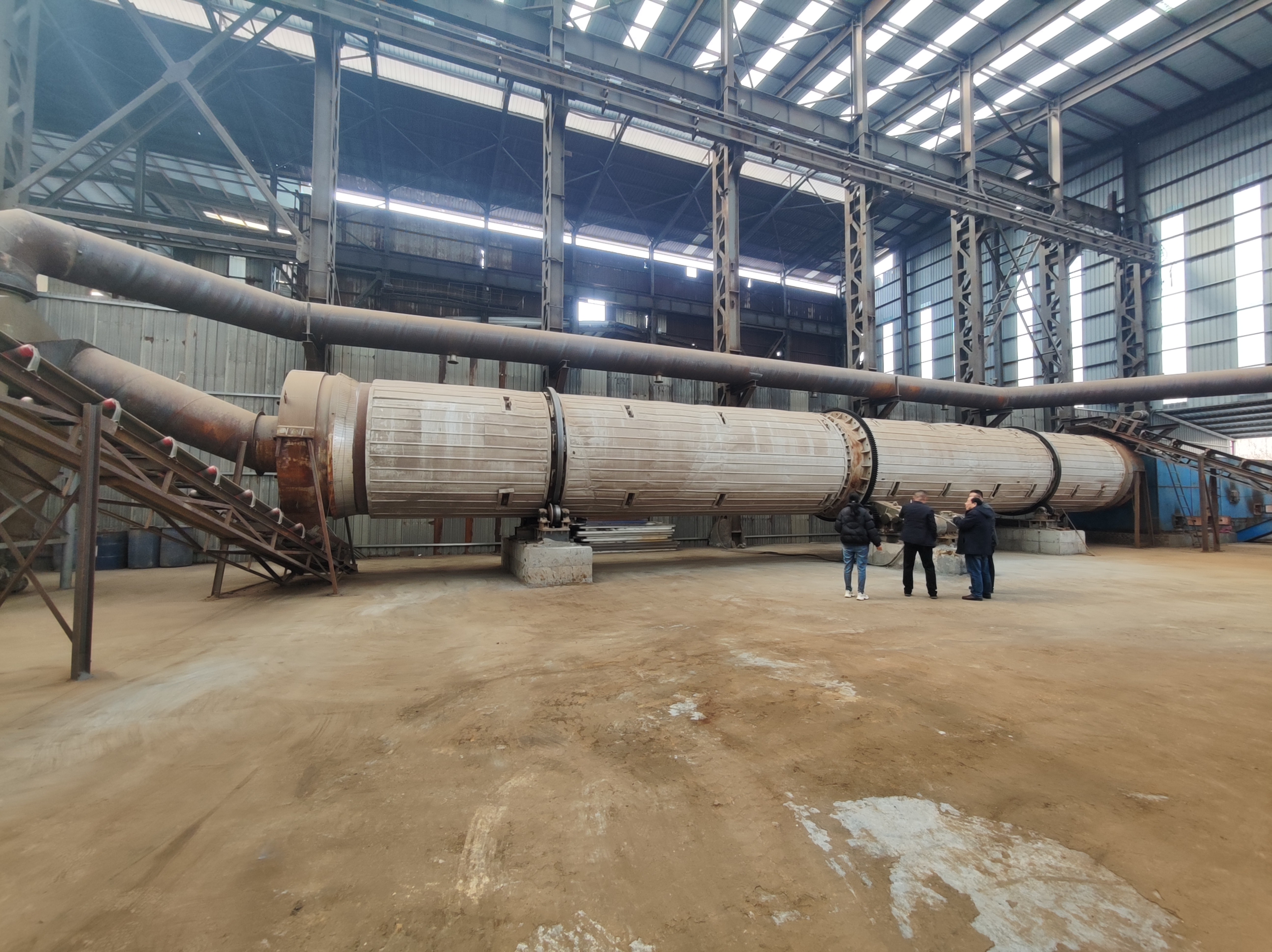
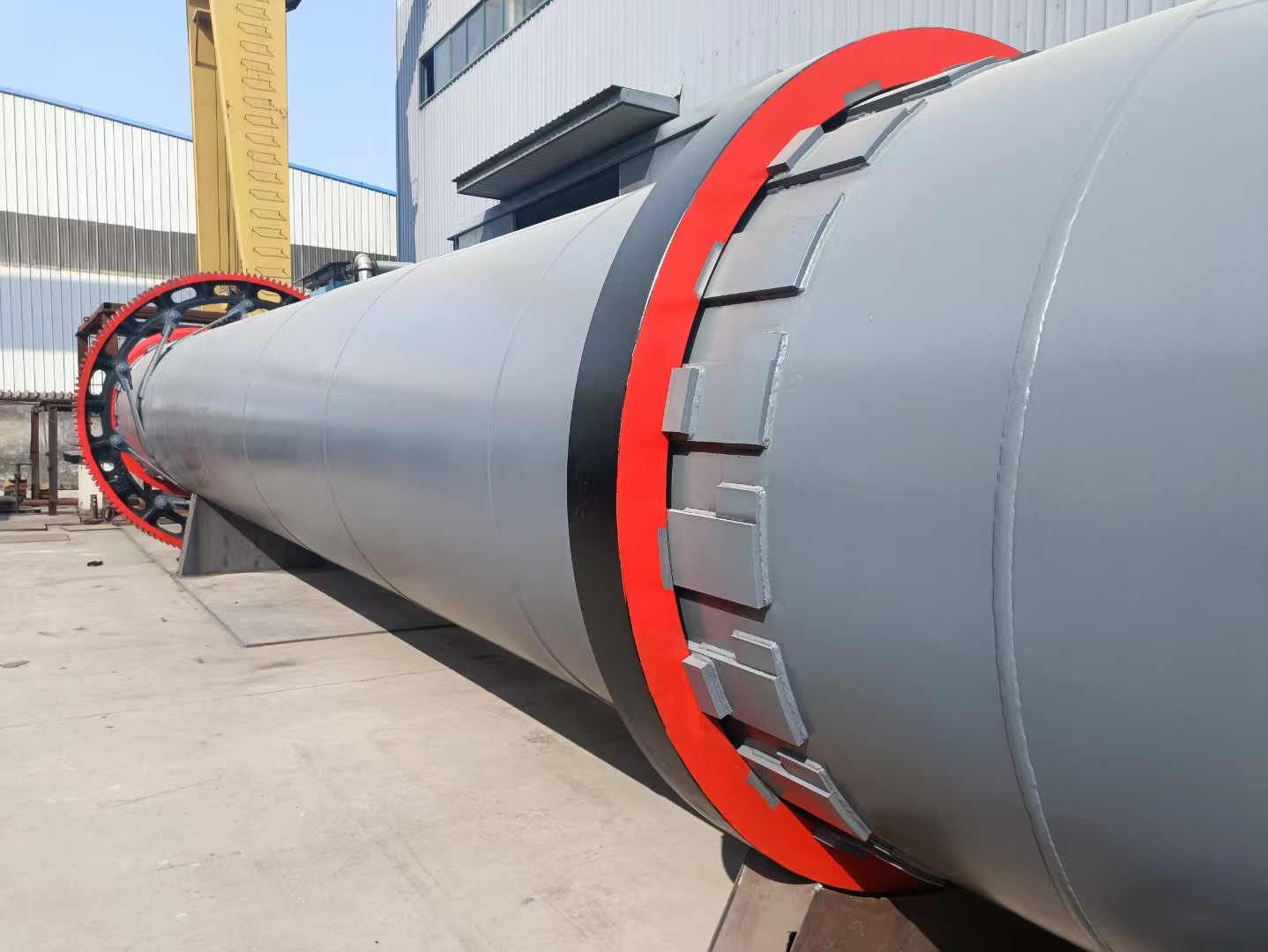
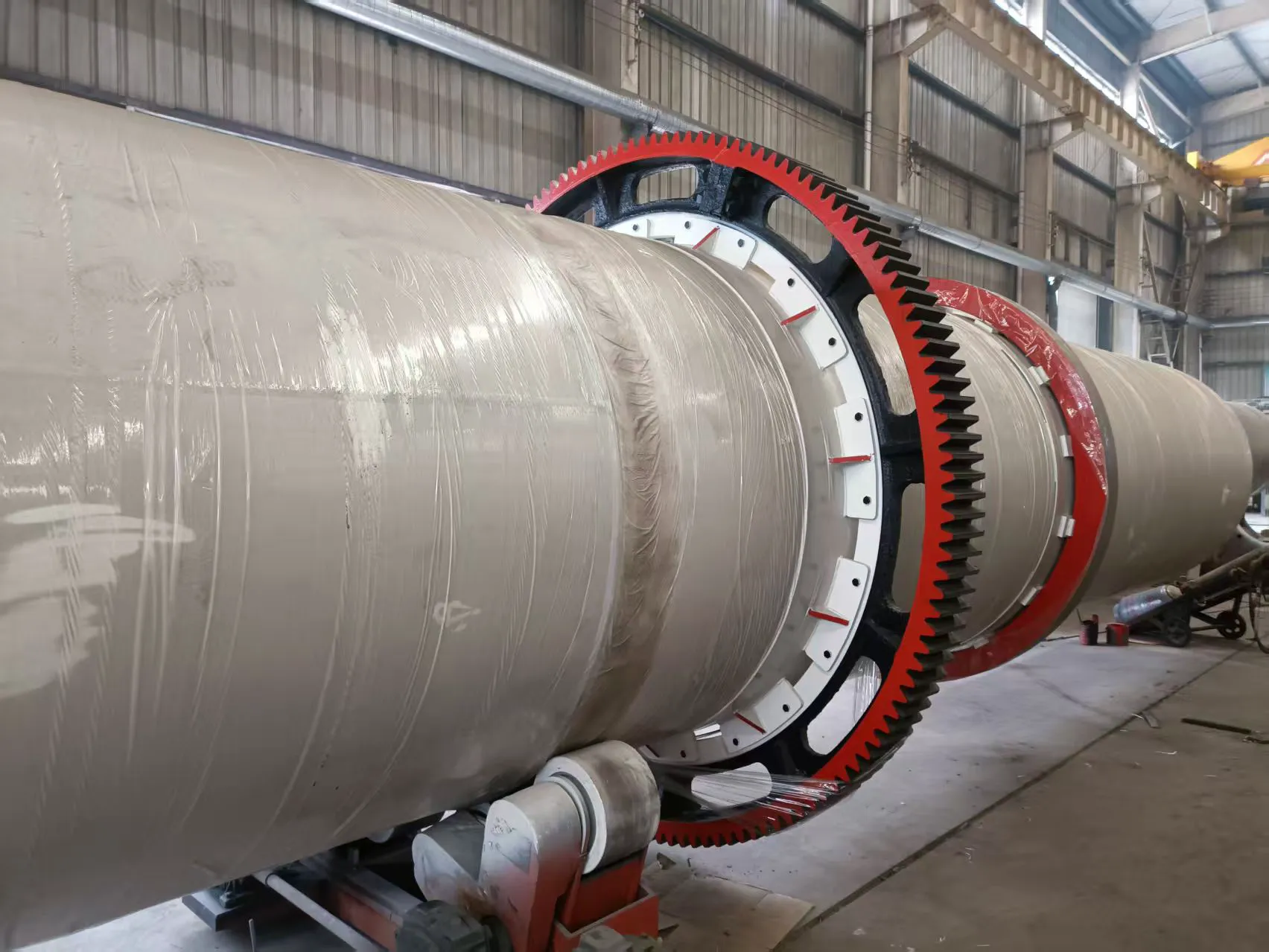
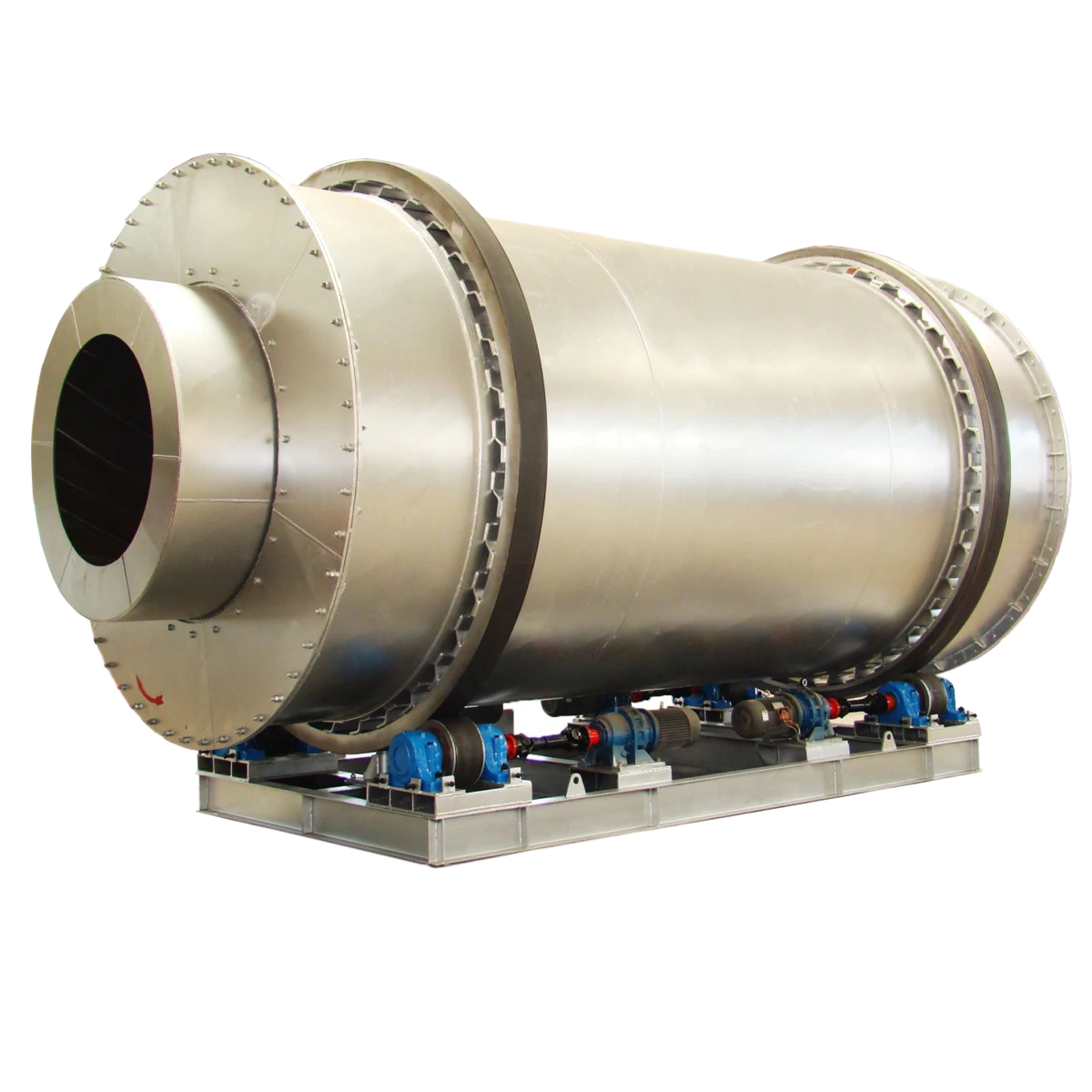
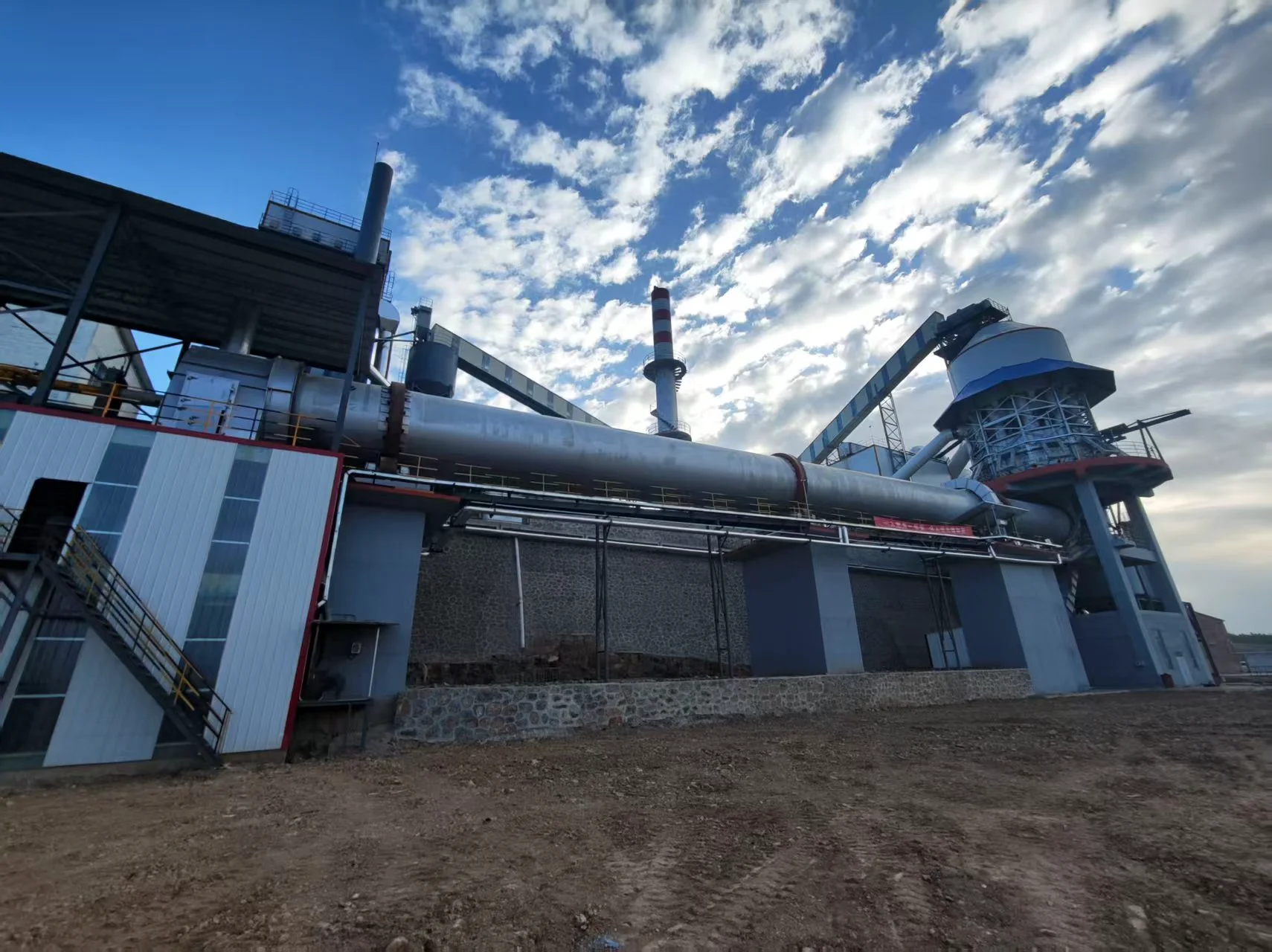
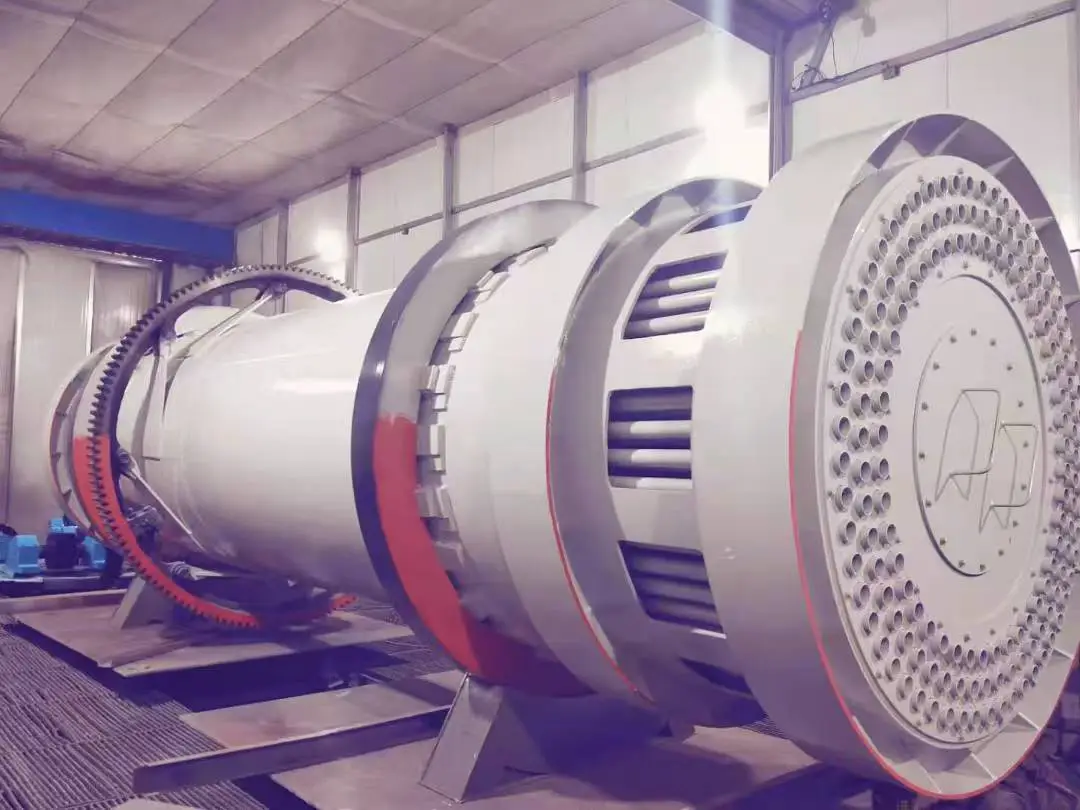
Sawdust dryer: including hot air furnace, feed port, rotating drum, filter drum, material conveying pipe, cooling drum and discharge port. The rotating drum is located on the active roller. The active roller drives the rotating drum to rotate at a low speed by the motor and the reduction transmission. A feed port is provided between the heating furnace and the rotating drum. Stir-frying blades are provided in the rotating drum. A baffle is provided at the connection between the rotating drum and the filter drum 4. A small hole is opened on the baffle. One end of the filter drum is connected to the rotating drum, and the other end is connected to the material conveying pipe. A block is provided in the filter drum. A slag discharge hole is provided at the bottom of the filter drum. One end of the cooling drum is connected to the material conveying pipe through a blower, and the other end is connected to the discharge port. Due to the above structure, the sawdust can be fully dried in the rotating drum, and the sawdust is fully dispersed again before entering the material conveying pipe, so that the water evaporates quickly. The block can block the impurities in the sawdust to ensure the quality of the sawdust entering the material conveying pipe. When the sawdust enters the sawdust dryer, the blowing pipe and the rotating cylinder work together to make the material boil and fluidize in the cylinder, and the hot air fully contacts the material to complete the drying.

Core design parameters:
parameter | Typical Value | explain |
|---|---|---|
Drum diameter | 1.2~3.5m | The larger the diameter, the higher the processing capacity, but the hot air distribution uniformity must be matched. |
Roller length | 6~26m | The aspect ratio is usually 4:1~8:1, and high moisture content requires a longer drying path. |
Tilt Angle | 3°~5° | Angle is adjustable, affecting the material residence time (usually 30~60 minutes) |
Speed | 2~8rpm | Frequency conversion control, sticky sawdust should be operated at low speed to prevent agglomeration. |
Hot air temperature | Inlet air 250~350℃/outlet air 80℃ | Hardwood (such as oak) can be heated to high temperatures, while softwood (pine) needs to be ≤300℃ to prevent resin volatilization. |
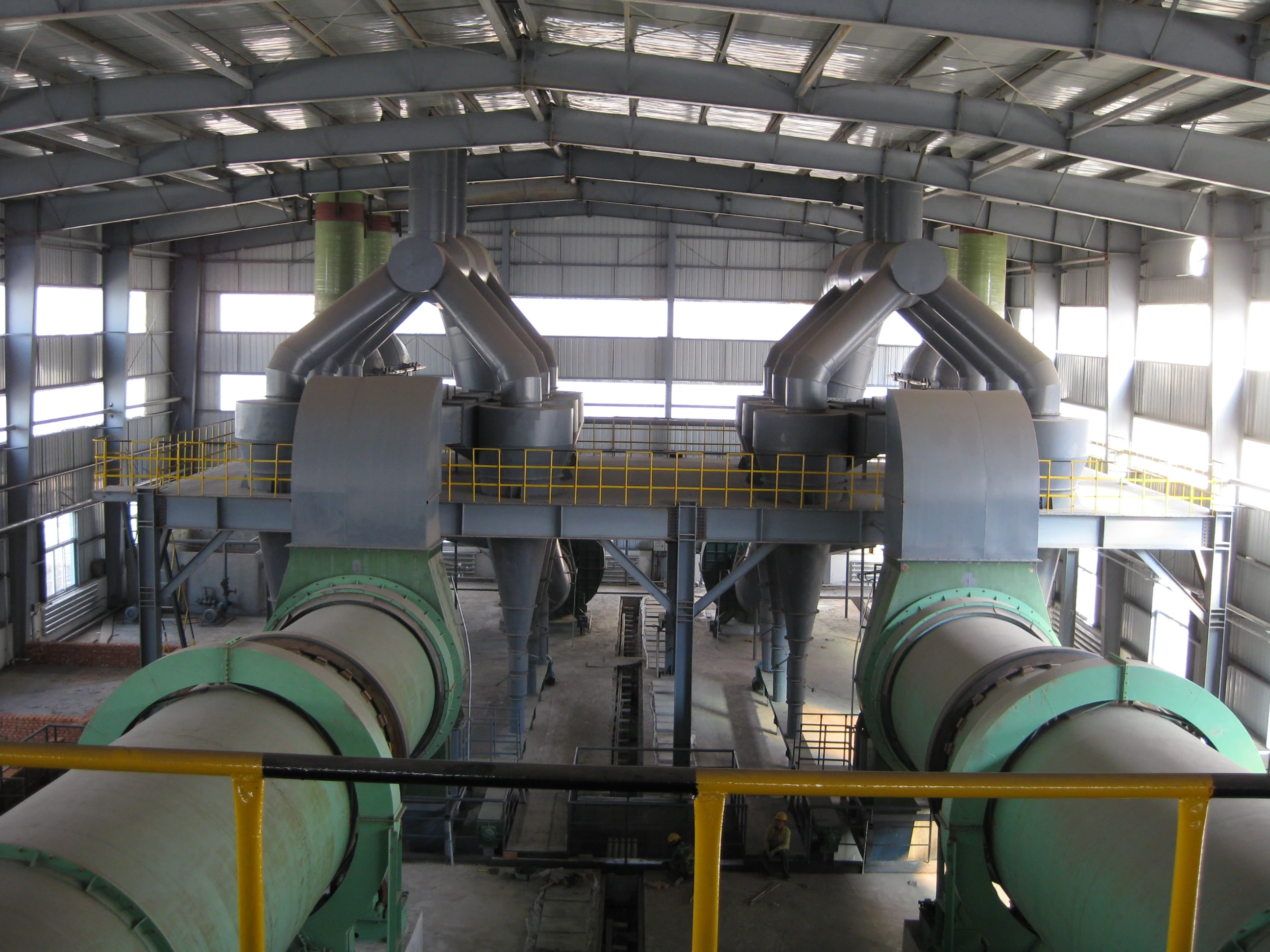

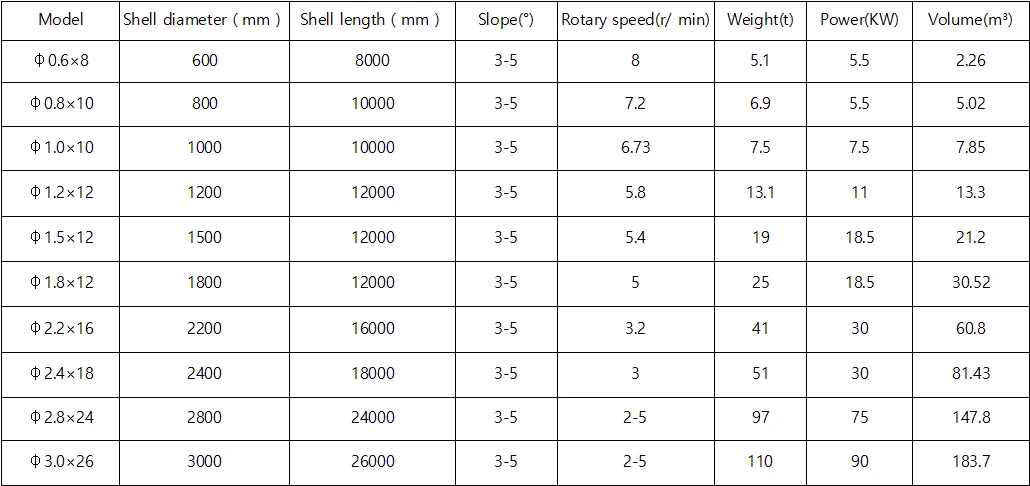
Technical Parameters: