Main features:
1. Uniform particles: By adjusting the disc inclination, rotation speed and spray volume, the size and shape of the particles can be controlled.
2. Flexible operation: The disc inclination and rotation speed are adjustable to meet the granulation needs of different materials.
3. Simple structure: The equipment has a compact structure, convenient maintenance and stable operation.
4. Wide applicability: It can be used for granulation of various materials such as fertilizers, feeds, ore powders, coal powders, etc.
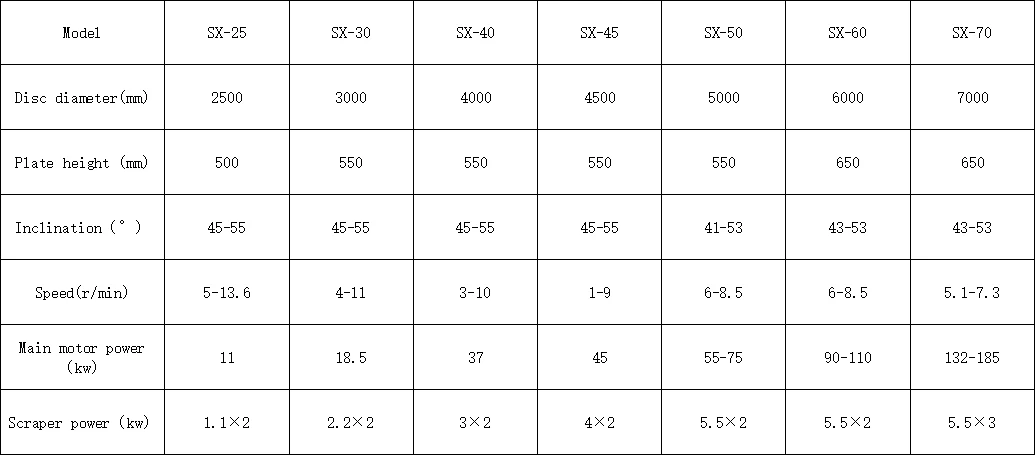
Technical Parameters:
Application areas:
Agriculture: used to produce compound fertilizers, organic fertilizers, feeds and other particles.
Chemical industry: used for granulation of catalysts, pigments, plastic particles, etc.
Metallurgy: used for granulation of mineral powders, metal powders, etc.
Environmental protection: used to treat wastes such as dust and sludge.
Working principle:
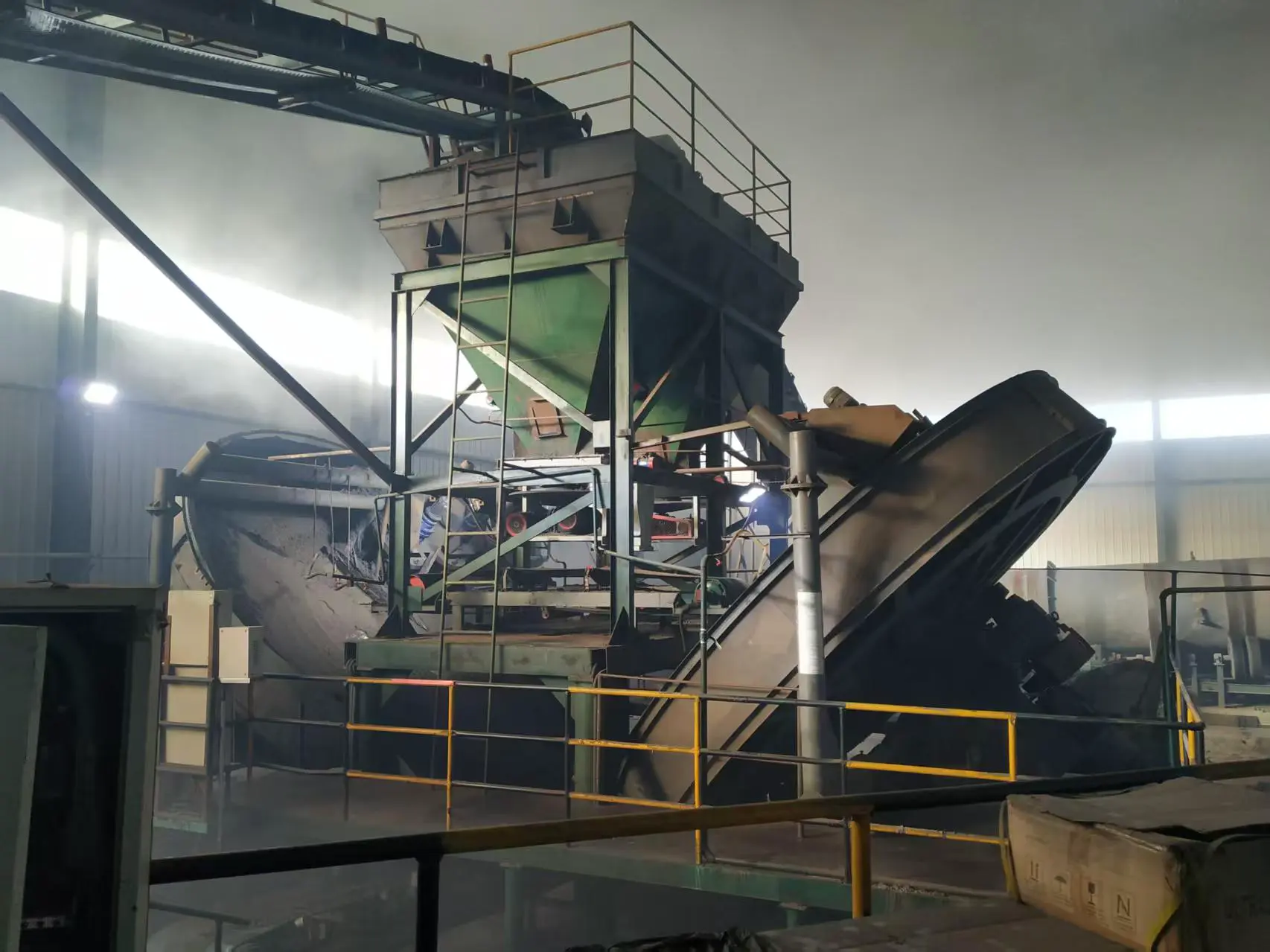
The main working part of the disc granulator is an inclined rotating disc. Powdery materials are added from the top of the disc, and an appropriate amount of liquid (such as water, adhesive, etc.) is sprayed at the same time. During the rotation of the disc, the material rolls continuously under the action of centrifugal force, gravity and friction, and gradually agglomerates into particles. The size of the particles is controlled by adjusting the disc inclination, rotation speed and spray volume.
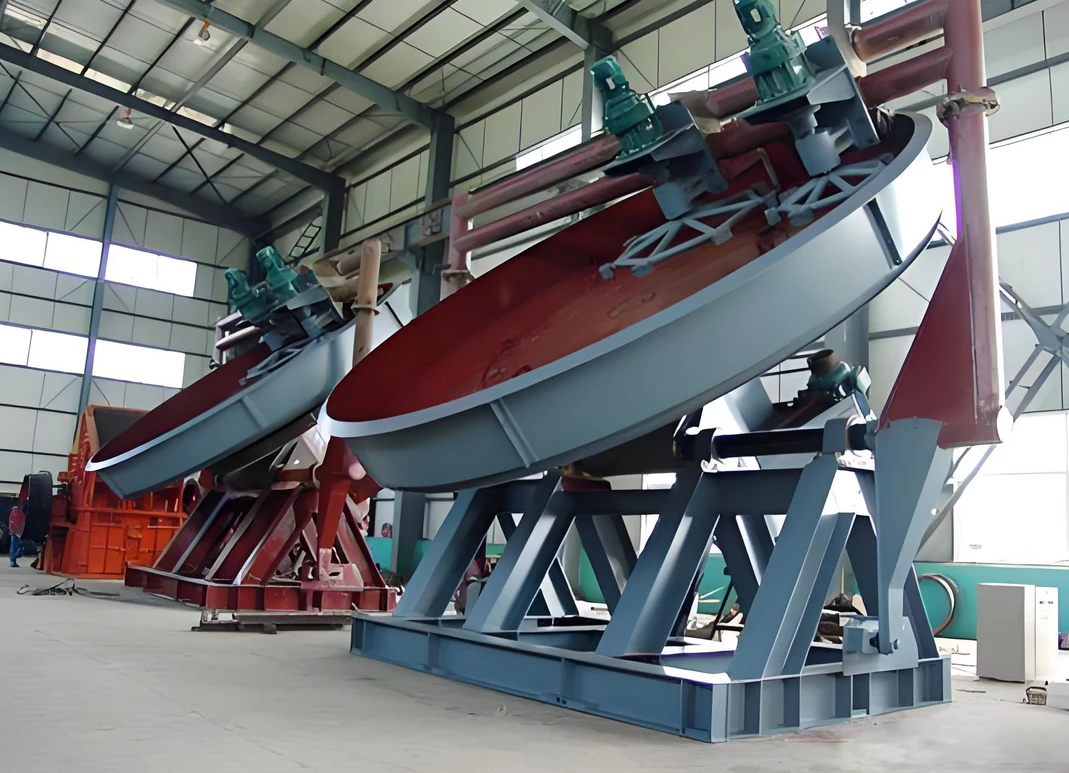

Equipment structure:
1. Disc: a rotating disc installed at an angle, used for rolling and agglomeration of materials.
2. Spraying system: spraying liquid on the material to promote particle formation.
3. Drive device: drives the disc to rotate, usually composed of a motor and a reducer.
4. Bracket: supports the disc and drive device, and can adjust the disc inclination.
Selection considerations:
1. Material characteristics: select a suitable disc granulator according to the particle size, humidity, viscosity, etc. of the material.
2. Production capacity: select equipment with suitable diameter and power according to production needs.
3. Particle requirements: adjust the disc inclination and rotation speed according to the particle size and shape requirements.
4. Material selection: select the disc material (such as stainless steel, carbon steel, etc.) according to the corrosiveness and wear resistance of the material.






















