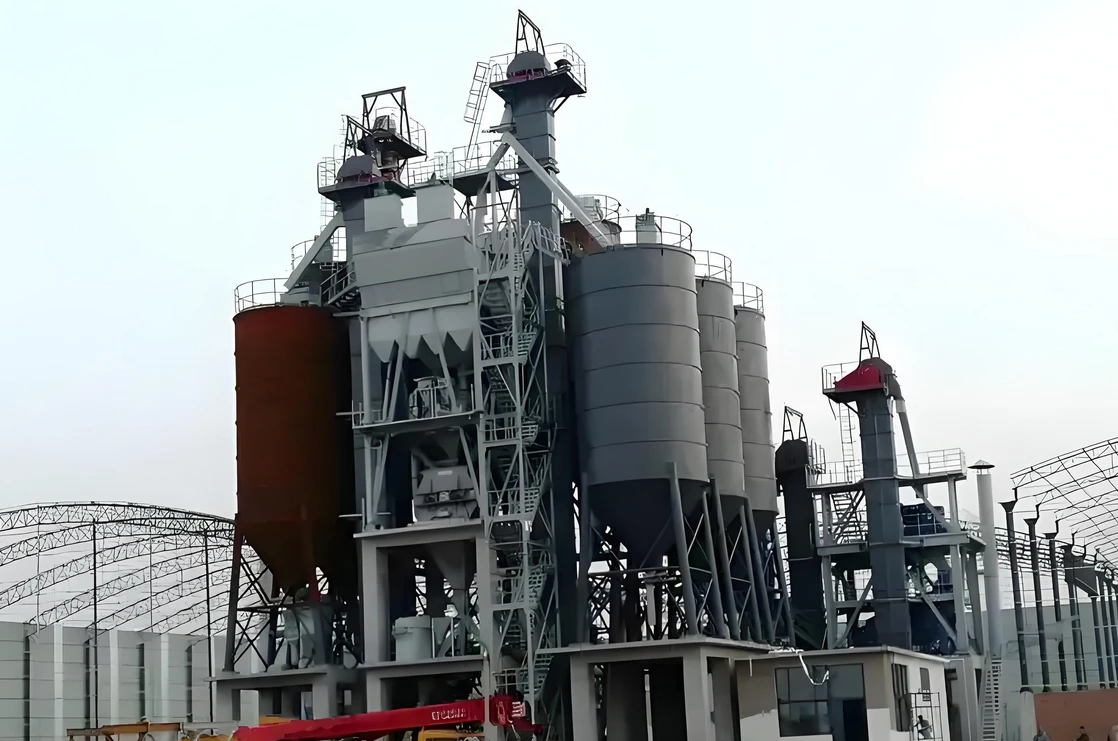
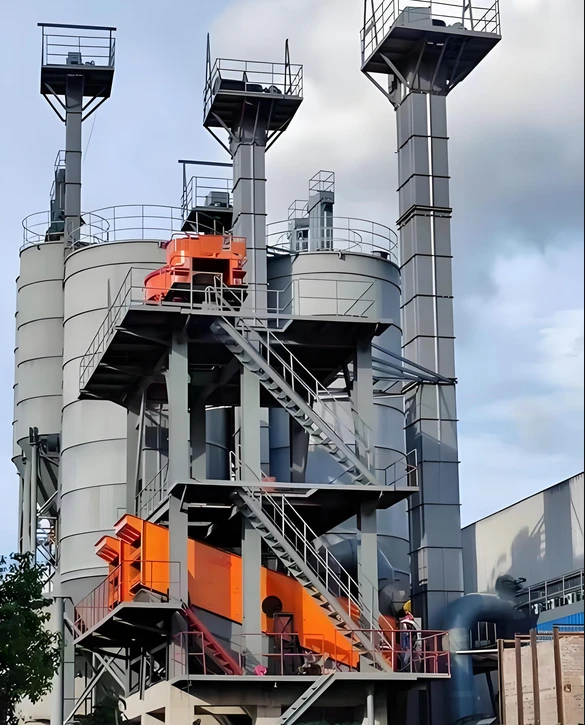
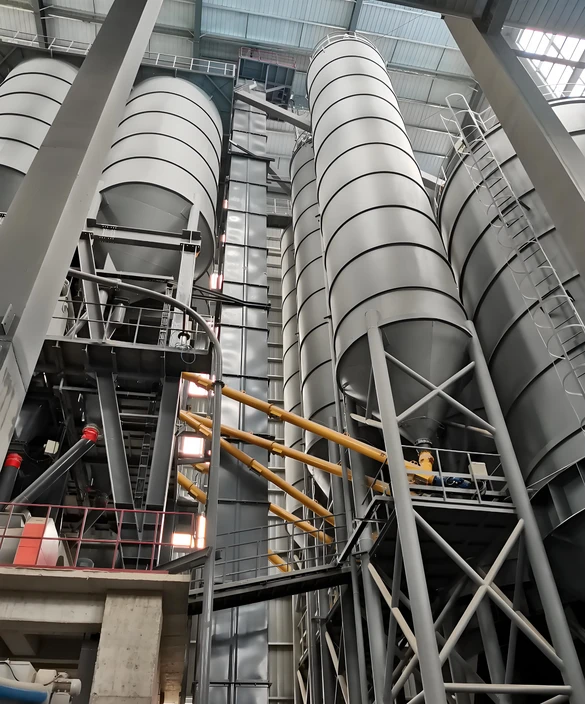
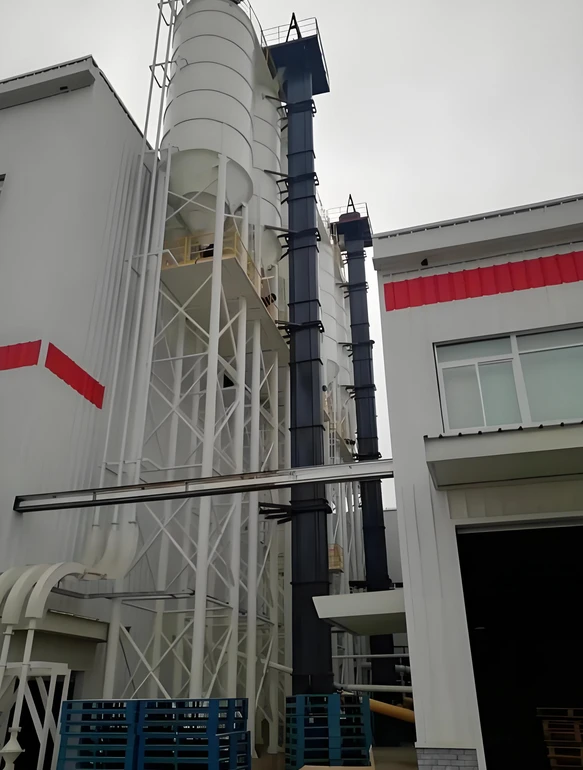
Main components
Hopper: a container for carrying materials, usually made of metal or plastic.
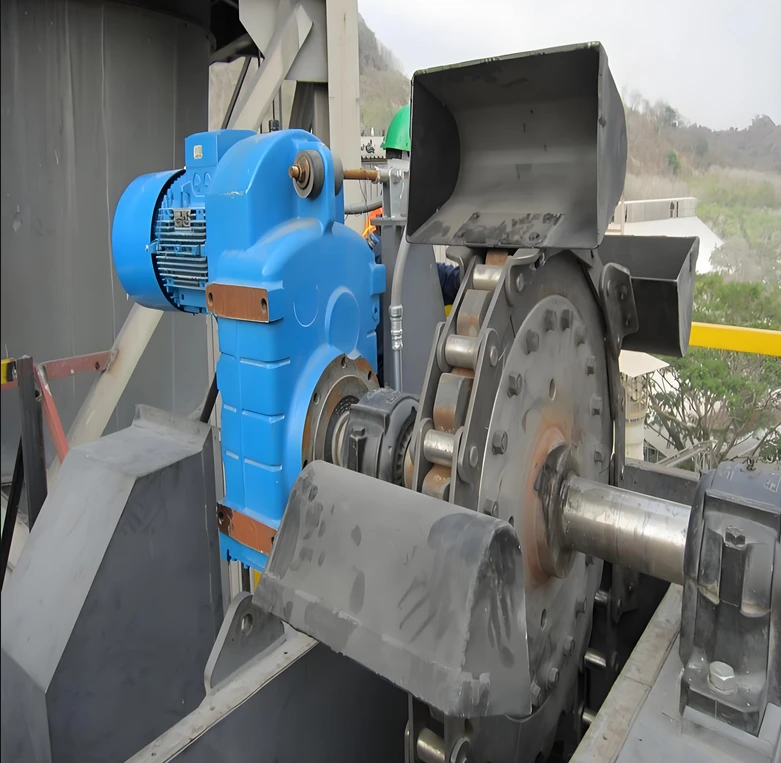
Chain or belt: a traction member that fixes the hopper and transmits power.
Drive device: includes a motor, a reducer and a drive wheel, providing power to move the chain or belt.
Head and tail: the head is the driving end and the tail is the tensioning end.
Shell: a closed structure to prevent material leakage and dust flying.
Tensioning device: maintain the proper tension of the chain or belt to prevent slipping or relaxation.
Working principle
The NE elevator drives the chain or belt to circulate through the drive wheel. The hopper loads the material at the bottom, lifts the material to the top with the movement of the chain or belt, and then unloads the material at the top by centrifugal force or gravity. The empty hopper returns to the bottom to complete a cycle.

Advantages
High efficiency: large conveying capacity, lifting height can reach tens of meters.
Good airtightness: the shell is closed to prevent material leakage and dust pollution.
Compact structure: small footprint, suitable for occasions with limited space.
Strong adaptability: can transport a variety of materials, including powder, granular and small pieces.
Application scenarios
Cement industry: transport cement, raw materials, coal powder, etc.
Chemical industry: transport fertilizers, plastic particles, etc.
Grain industry: transport grains, feed, etc.
Metallurgical industry: transport ore, slag, etc.
Common types
Centrifugal unloading: use centrifugal force to throw materials out of the hopper, suitable for transporting materials with good fluidity.
Gravity unloading: use the material's own gravity to unload, suitable for transporting materials with poor fluidity.
Mixed unloading: combine centrifugal and gravity unloading, suitable for transporting a variety of materials.
Common problems and solutions
Hopper wear: check the hopper status regularly and replace the hopper with severe wear.
Chain or belt breakage: check the wear of the chain or belt and replace it in time.
Material blockage: adjust the feed amount and clean the blocked parts.
Excessive noise: check the tension of the chain or belt, and lubricate the chain and drive wheel.
Maintenance
Regularly check hoppers, chains or belts for wear.
Lubricate chains and drives.
Clear housing of material buildup.
Check tensioners to ensure proper chain or belt tension.



















