Structure and working principle
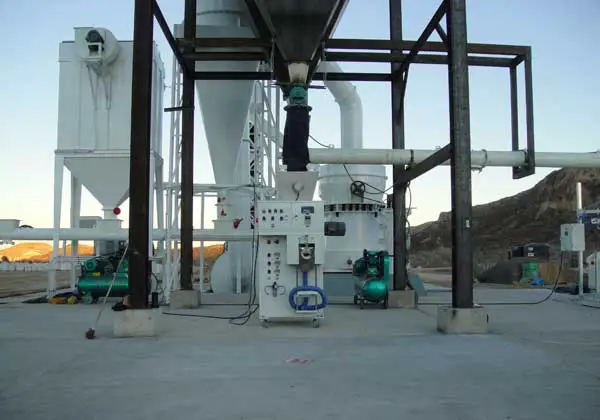
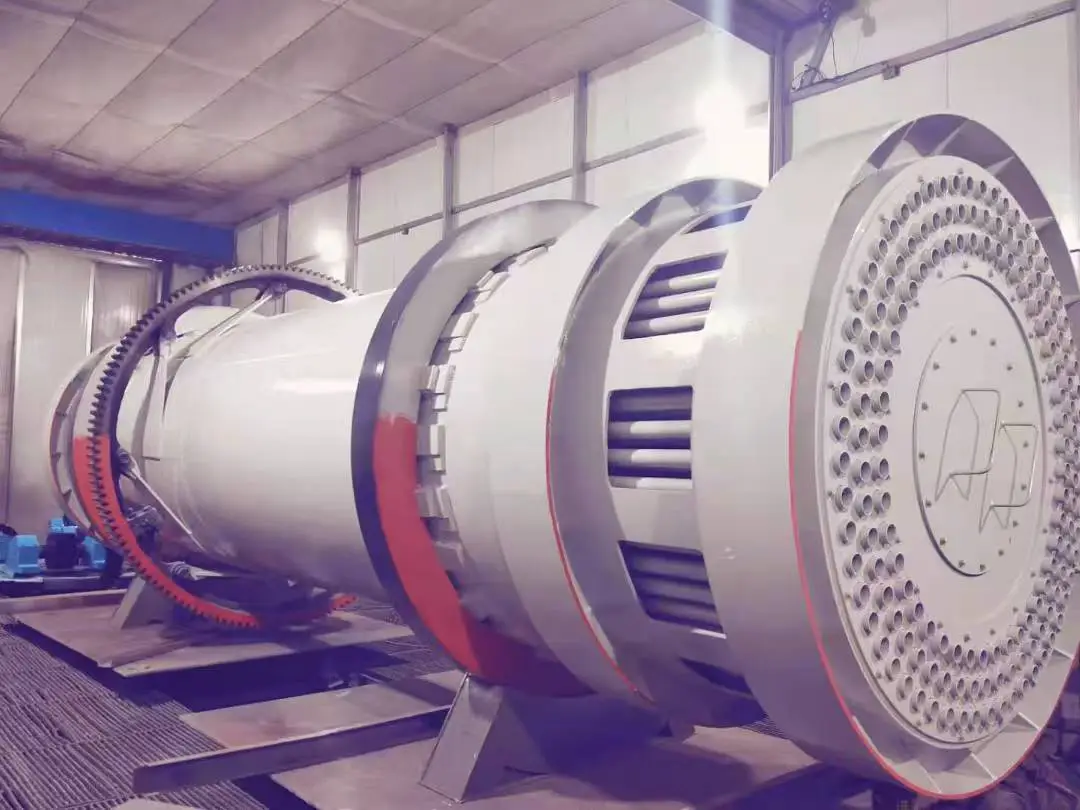
(1) Main structure
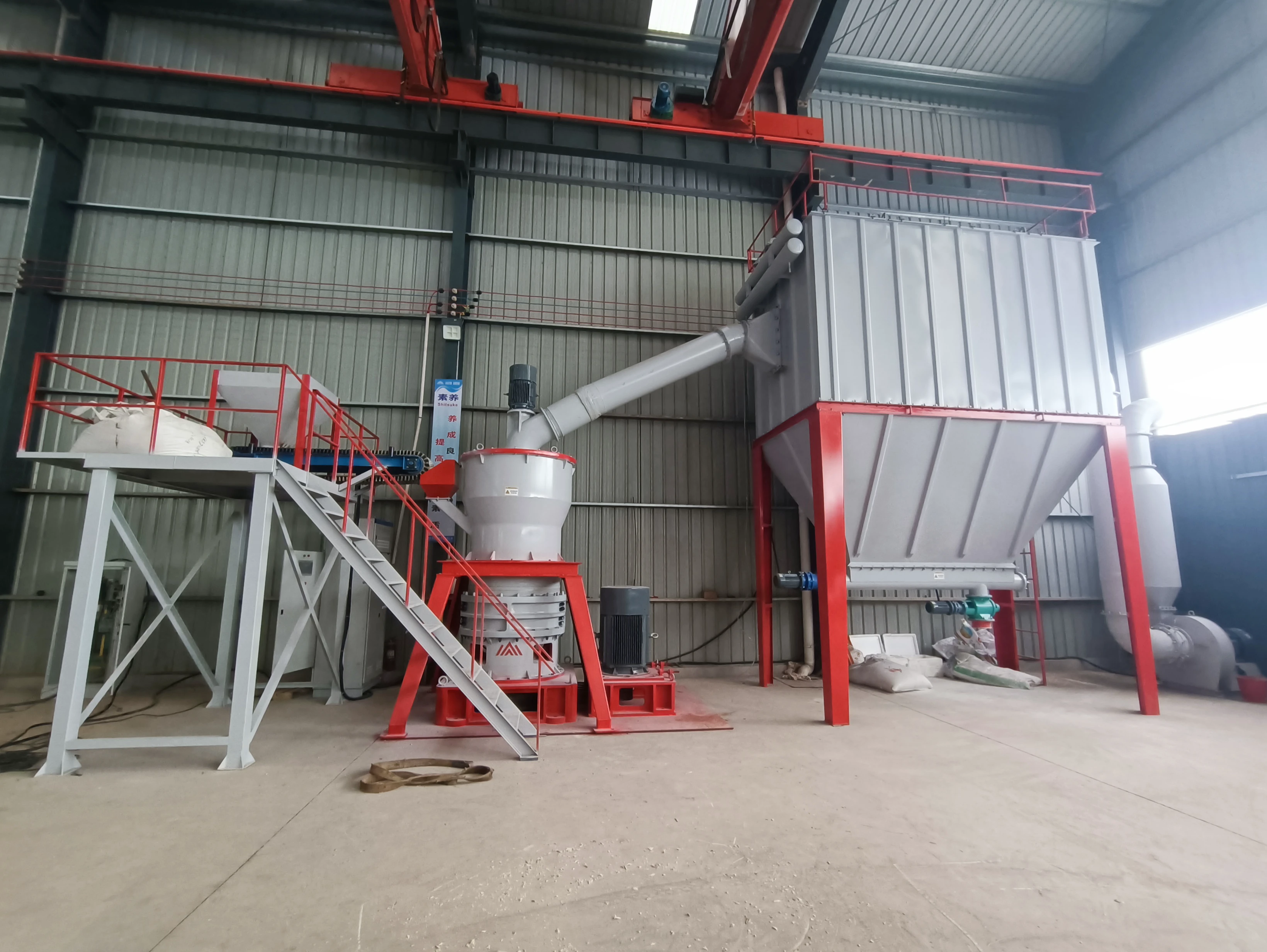
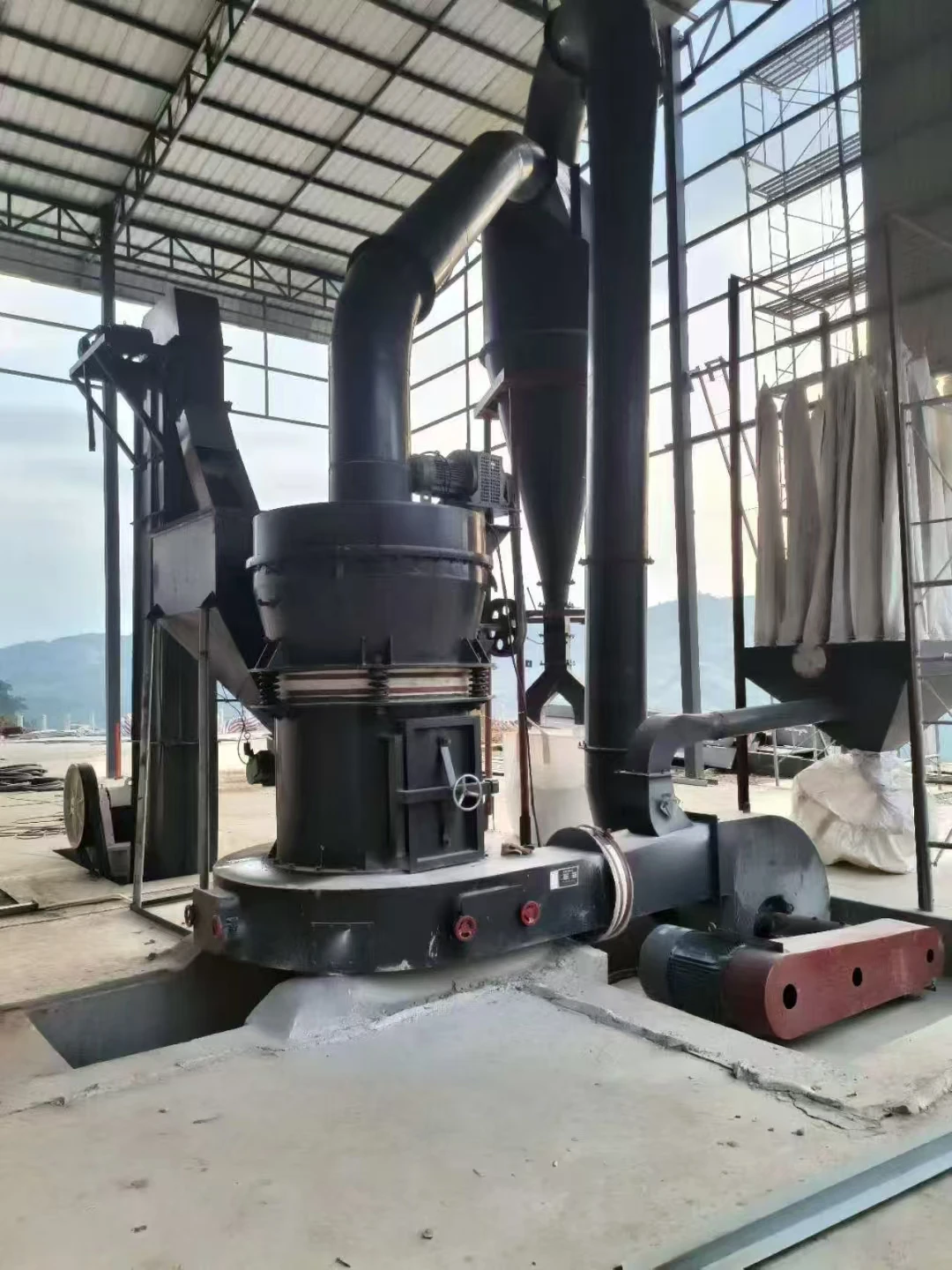
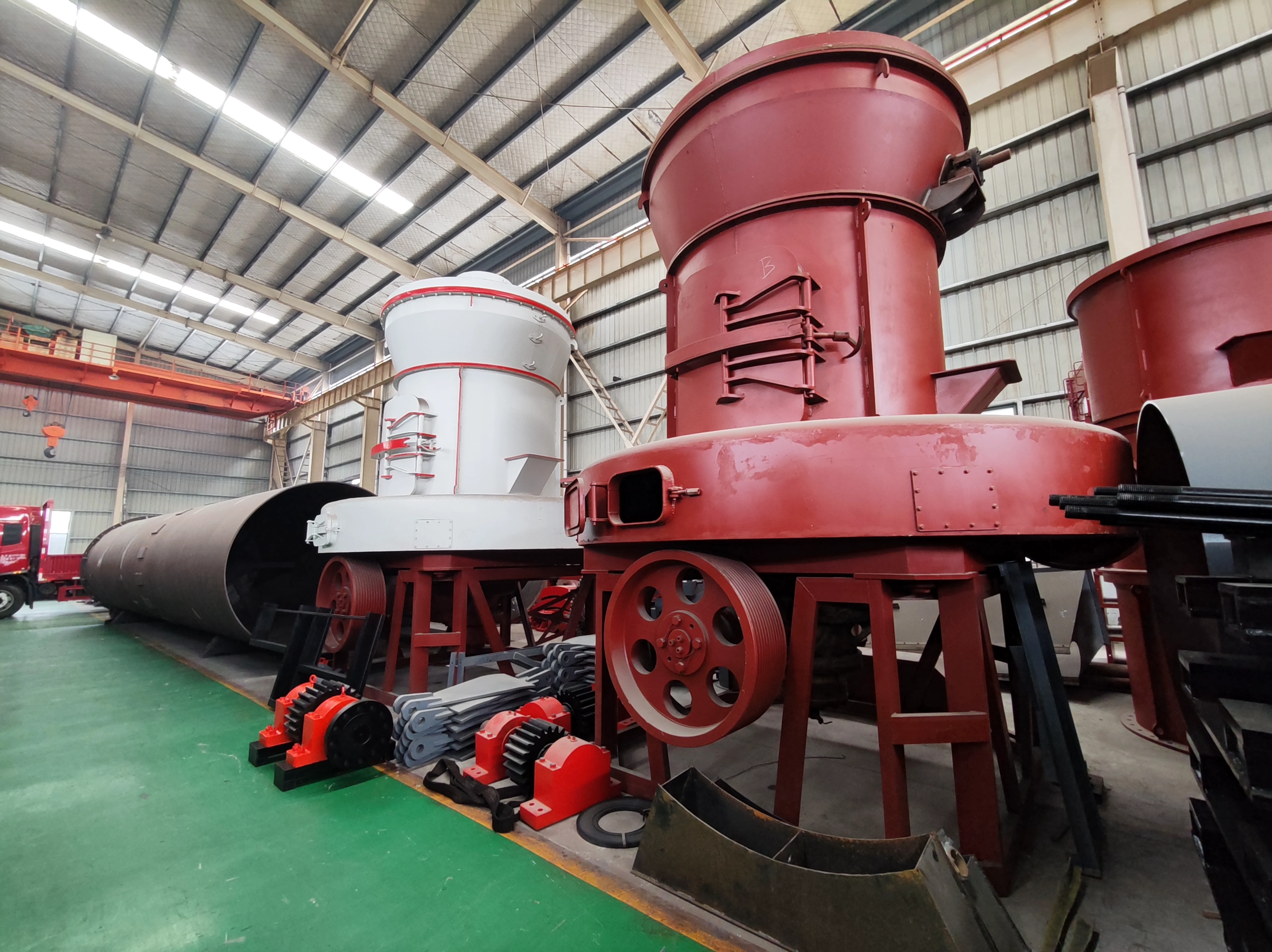
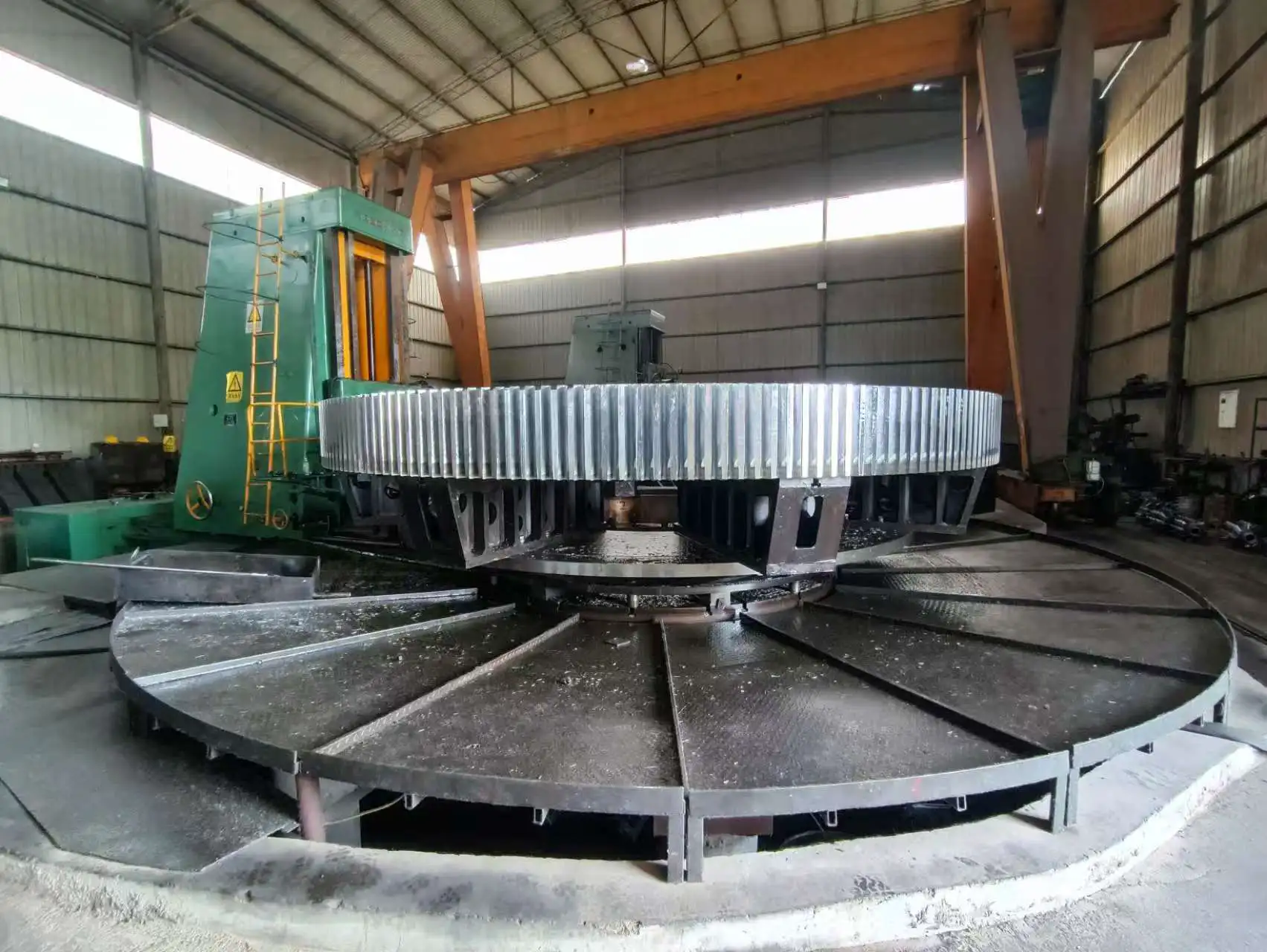
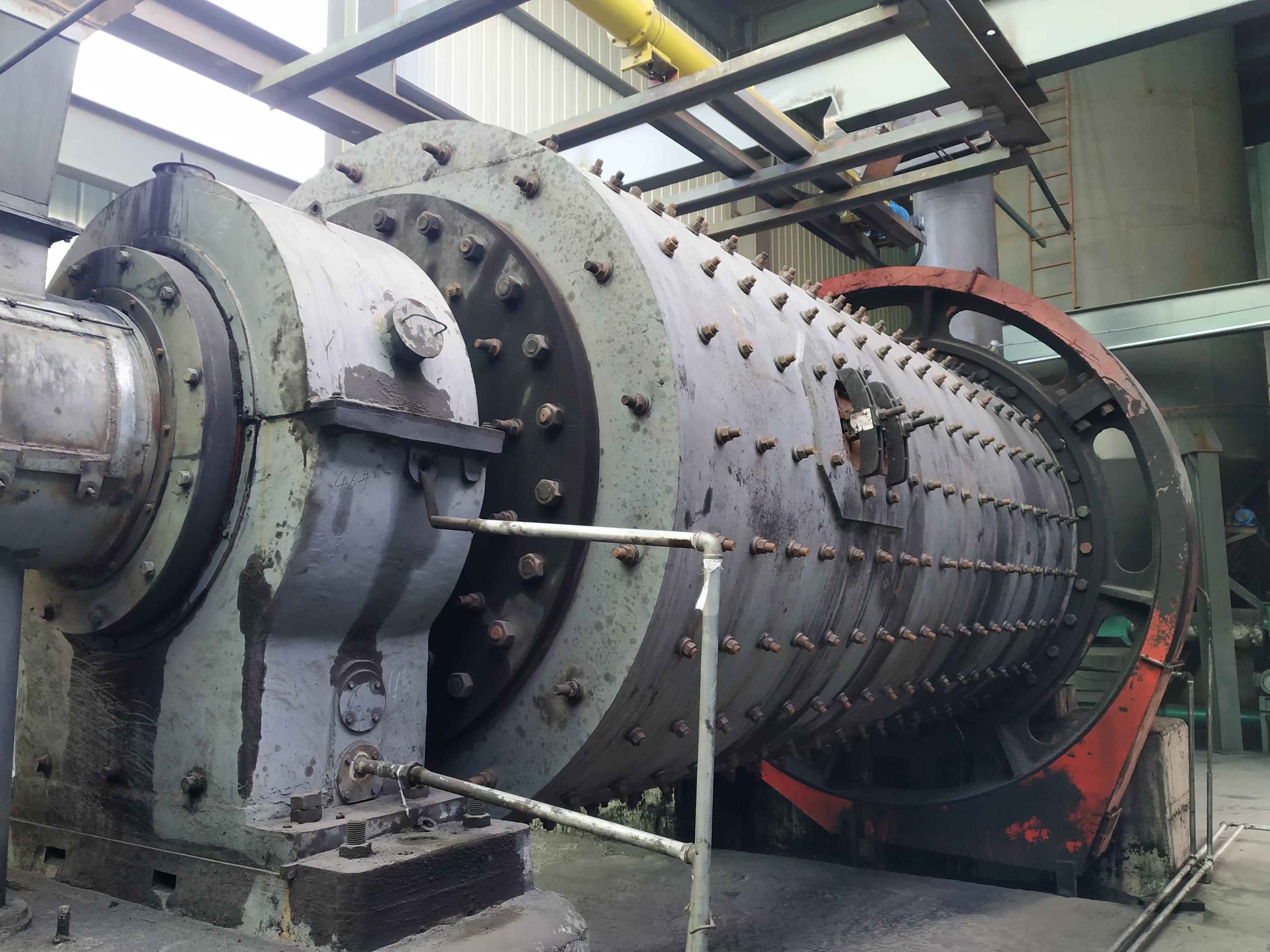
Main unit: It consists of a frame, air inlet volute, grinding ring, grinding roller (3 layers), main shaft assembly, classifier, etc.
Transmission system: The motor drives the main shaft to rotate through the reducer, and the grinding roller crushes the material under the action of centrifugal force.
Classification system: Built-in turbine classifier to control the fineness of the finished product.
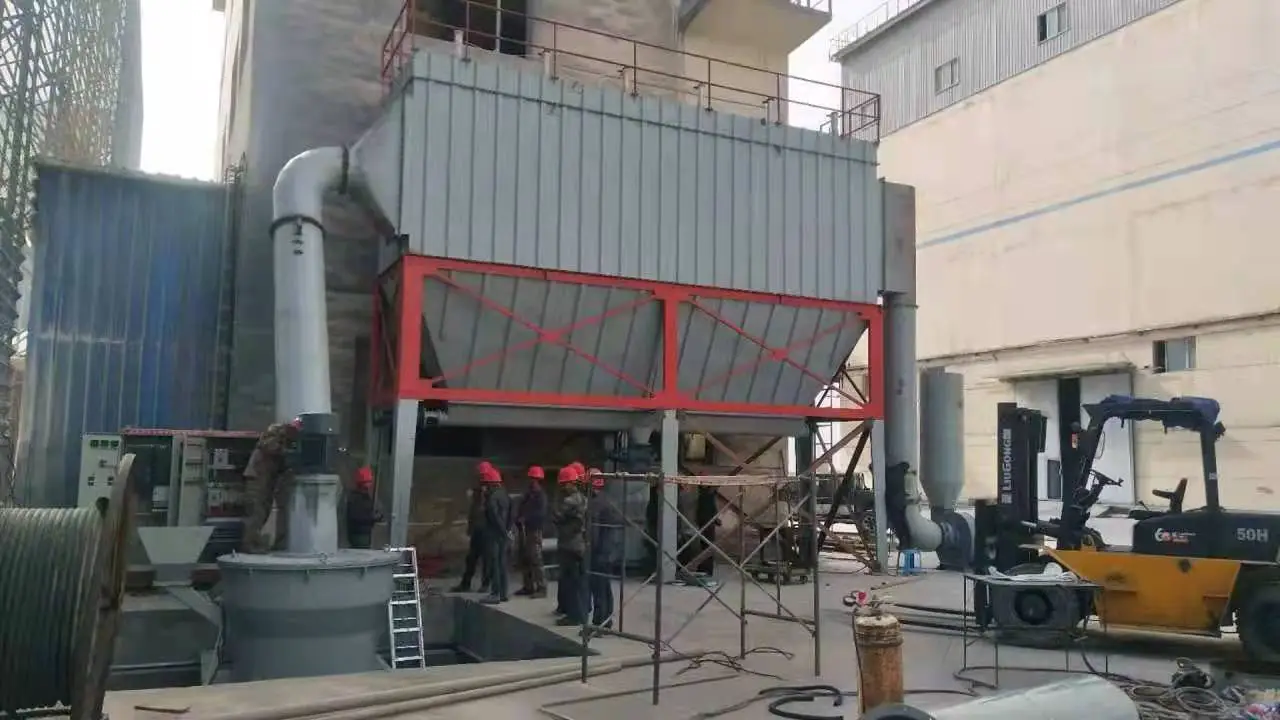
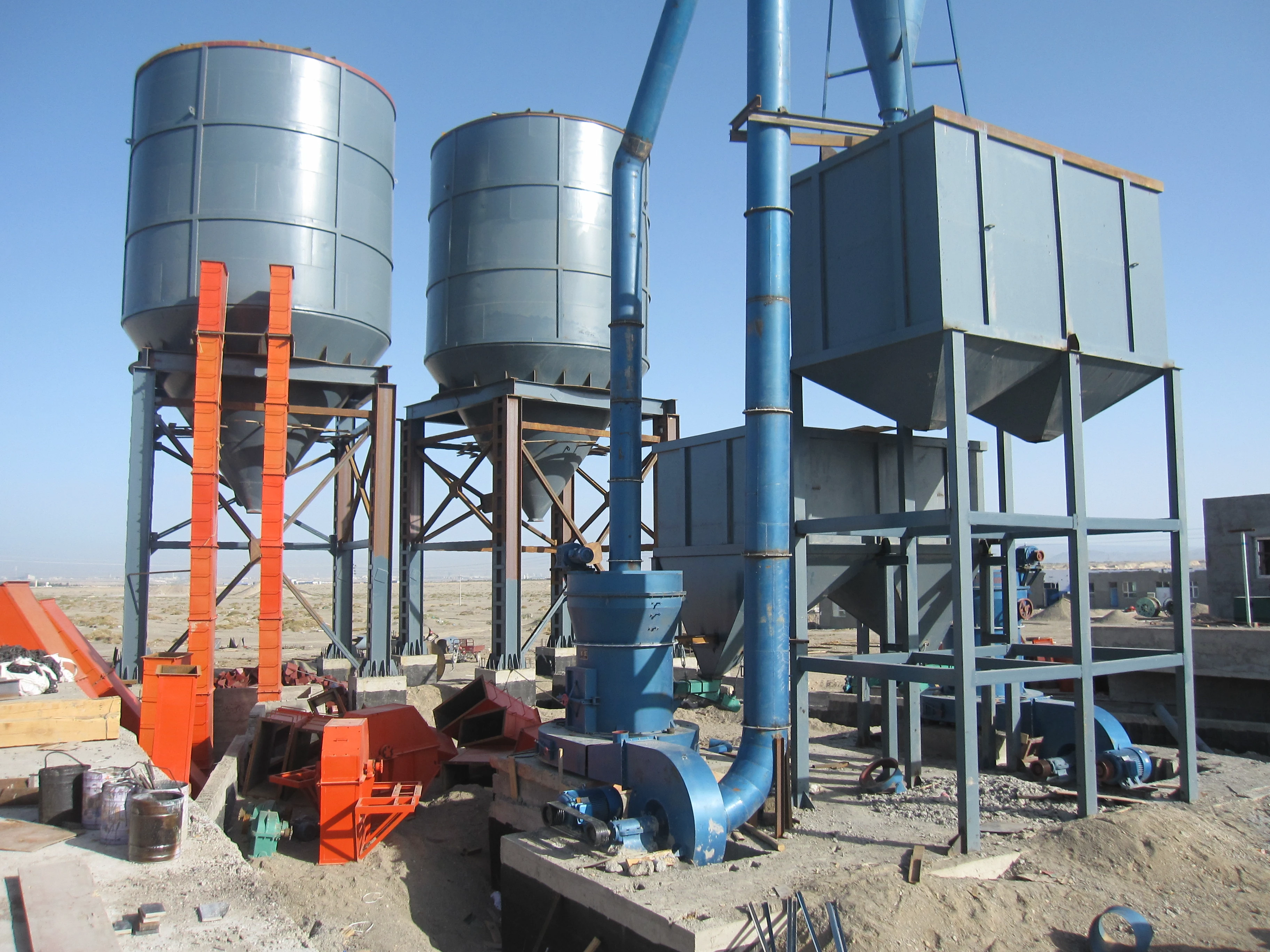
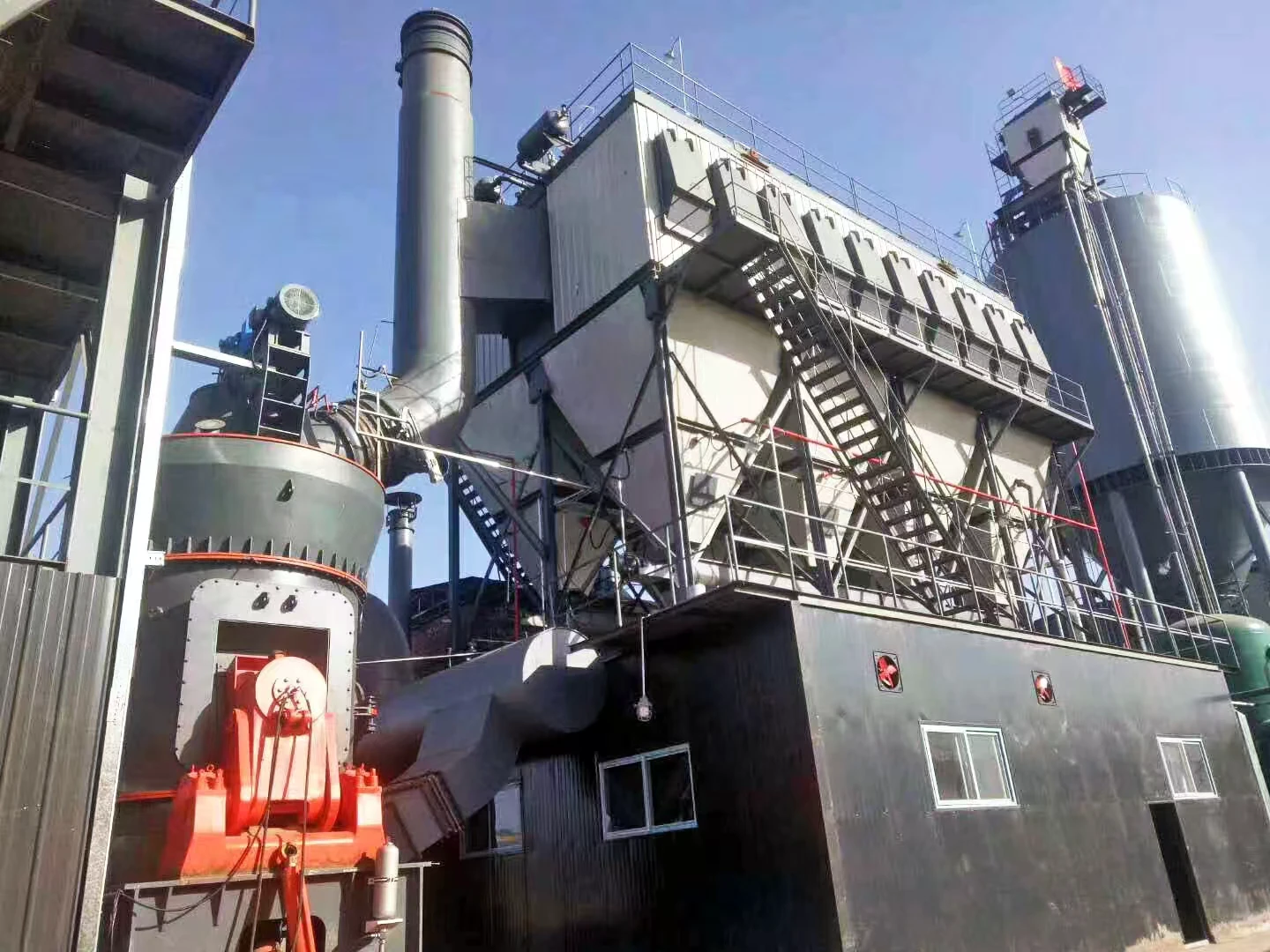
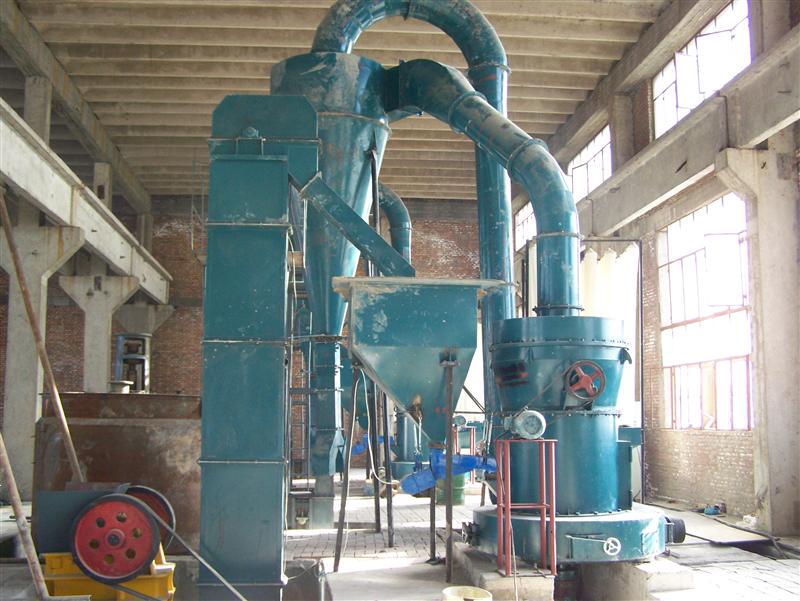
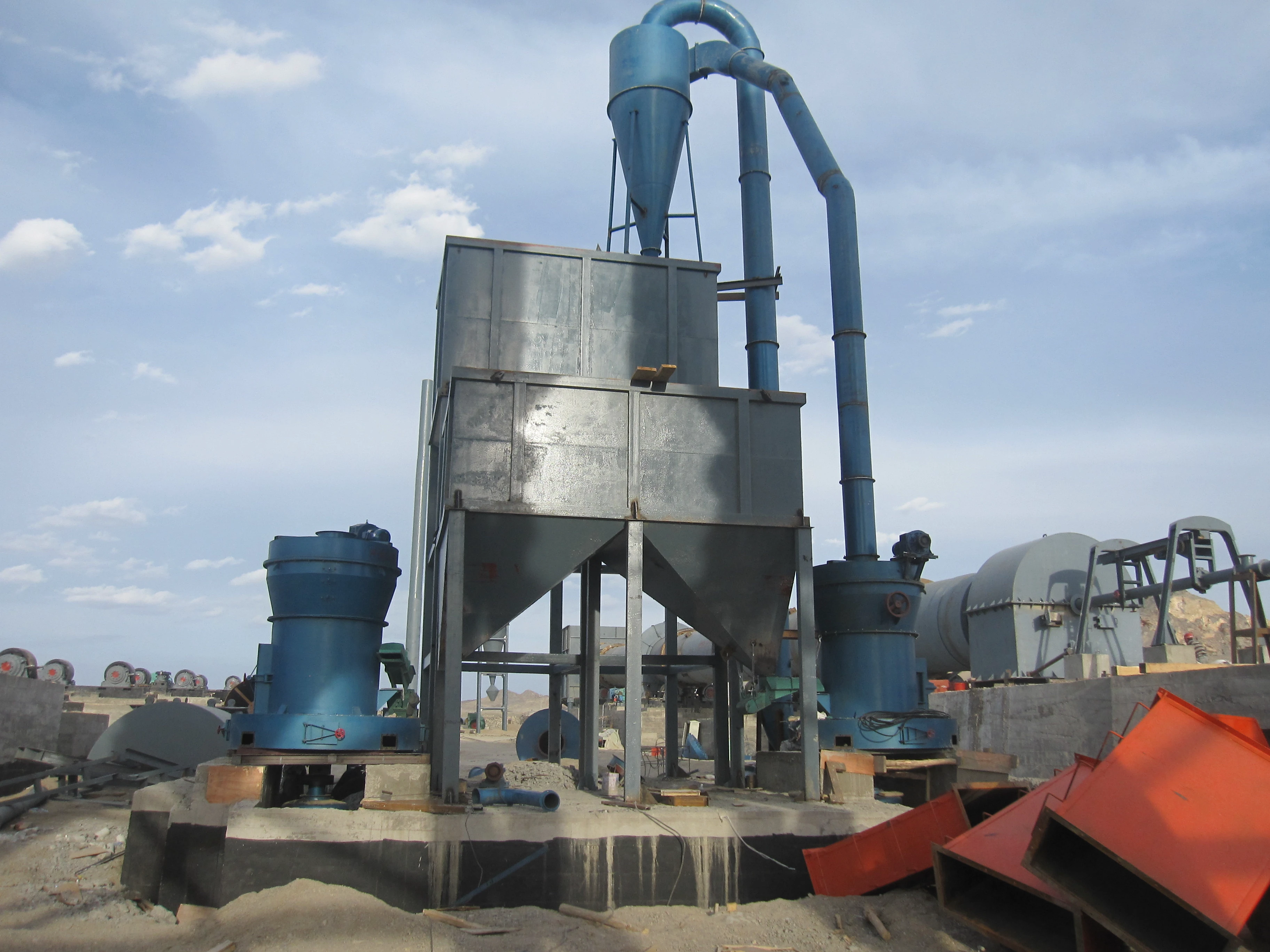
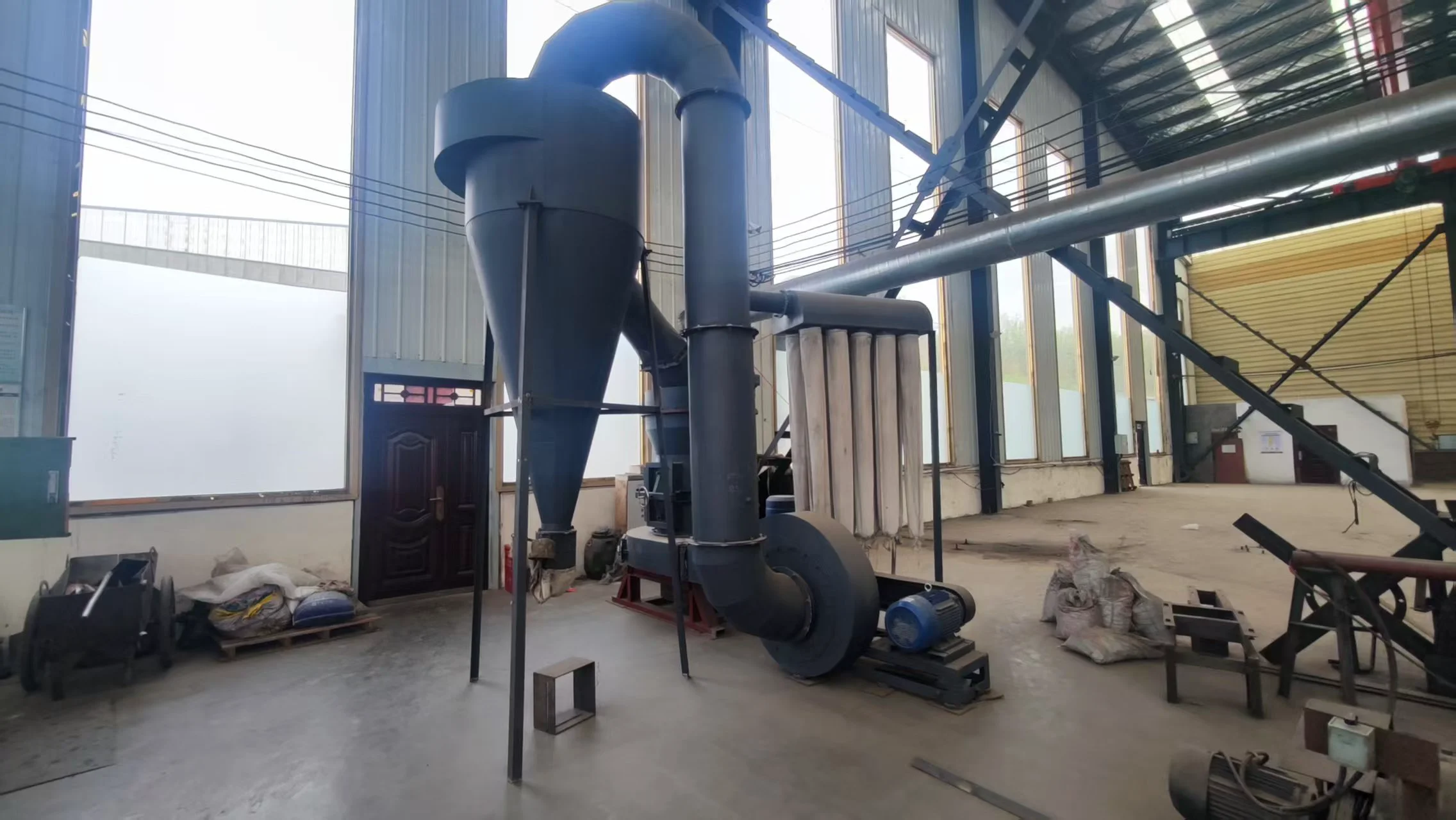
Auxiliary equipment: Cyclone collector, pulse dust collector, fan, etc.
(2) Working principle
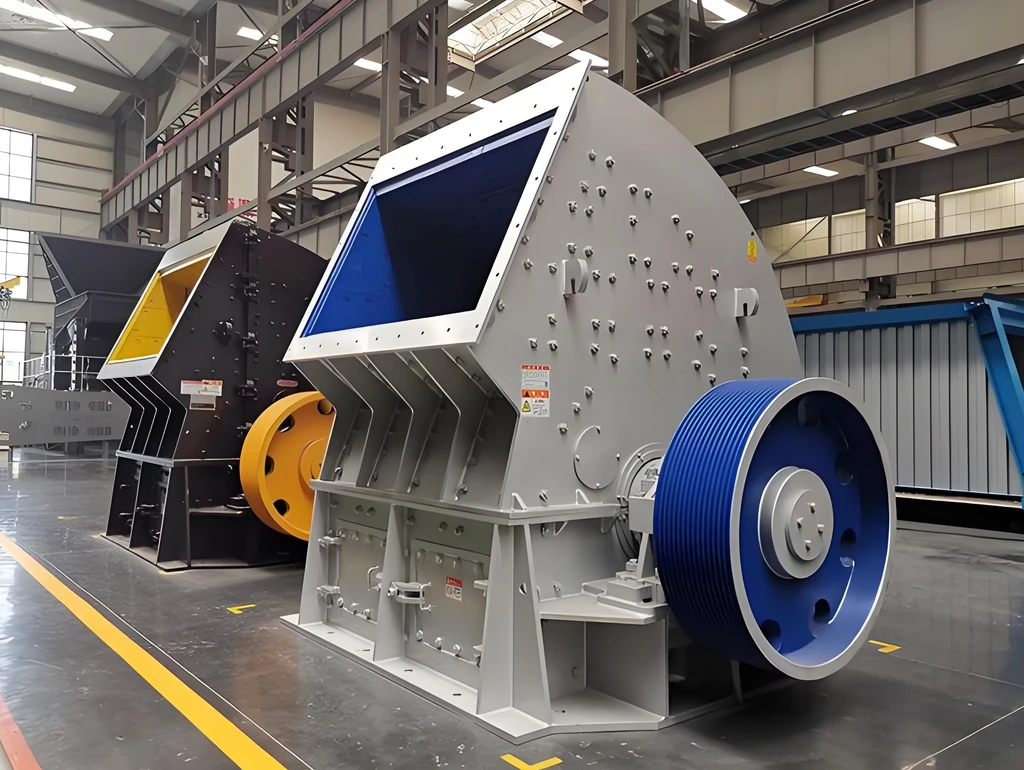
1. Crushing stage: After the material is initially crushed by the jaw crusher, it is sent to the main unit of the mill by the elevator.
2. Grinding stage: The material falls between the grinding ring and the grinding roller, and is repeatedly crushed, sheared and crushed by the three layers of grinding rollers.
3. Classification stage: The crushed powder is blown up by the air flow, screened by the classifier, and the qualified fine powder enters the collection system, and the coarse powder returns to the re-grinding.
4. Collection stage: The finished powder is collected by the cyclone separator and dust collector, and the exhaust gas is discharged after purification.
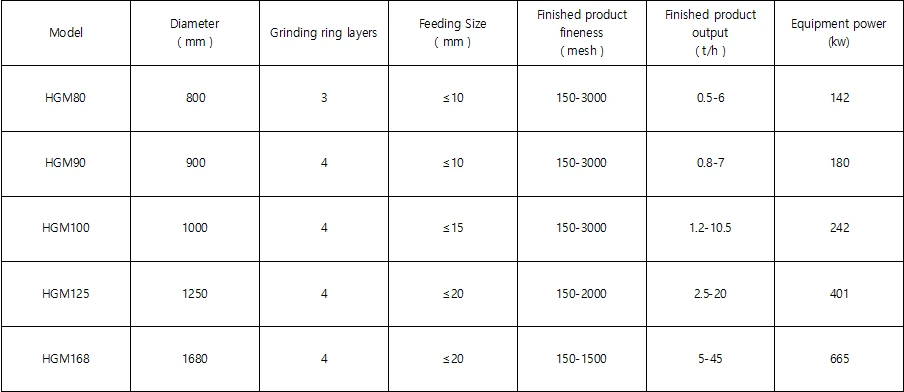
Technical Parameters
Core Features
Three-ring design: adopts three-layer grinding roller and grinding ring structure, with longer grinding track and higher efficiency.
Medium-speed operation: the spindle speed is moderate (about 100-200rpm), balancing energy consumption and wear.
High fineness and high yield: the finished product fineness can be adjusted between **400-2500 mesh**, and the output is more than 30% higher than that of traditional Raymond mill.
Energy saving and environmental protection: the pulse dust removal system makes the dust emission concentration lower than the national environmental protection standard.
-Low wear: the grinding roller and grinding ring are made of high-hardness alloy material with long service life.
Applicable materials
Non-metallic minerals: calcite, marble, barite, talc, bentonite, kaolin, etc.
Chemical raw materials: gypsum, graphite, fluorite, carbon, etc.
Others: ceramic raw materials, refractory materials, pesticide powder, etc.

Advantages and limitations
Advantages
Flexible fineness adjustment to meet various industrial needs.
Compact structure and small footprint.
Stable operation, low vibration and noise.
Limitations
Materials with moisture content > 6% need to be dried in advance.
Replacement and maintenance of grinding rollers require professional operation.
Selection suggestions
Fineness requirements: If ultrafine powder above 2500 mesh is required, it is recommended to use it with air flow mill.
Output matching: Select the model according to the production scale (such as HGM100 is suitable for small and medium-sized production lines).
Material characteristics: Avoid iron impurities or high-hardness materials to avoid damage to the grinding roller.
Maintenance and care
Regular lubrication: The main shaft and grinding roller bearings need to be filled with high-temperature grease every 500 hours.
Wear inspection: The thickness of the grinding roller and grinding ring is checked every 3-6 months, and the wear exceeds the limit and needs to be replaced.
Classifier cleaning: Prevent powder adhesion from affecting the classification accuracy.
























