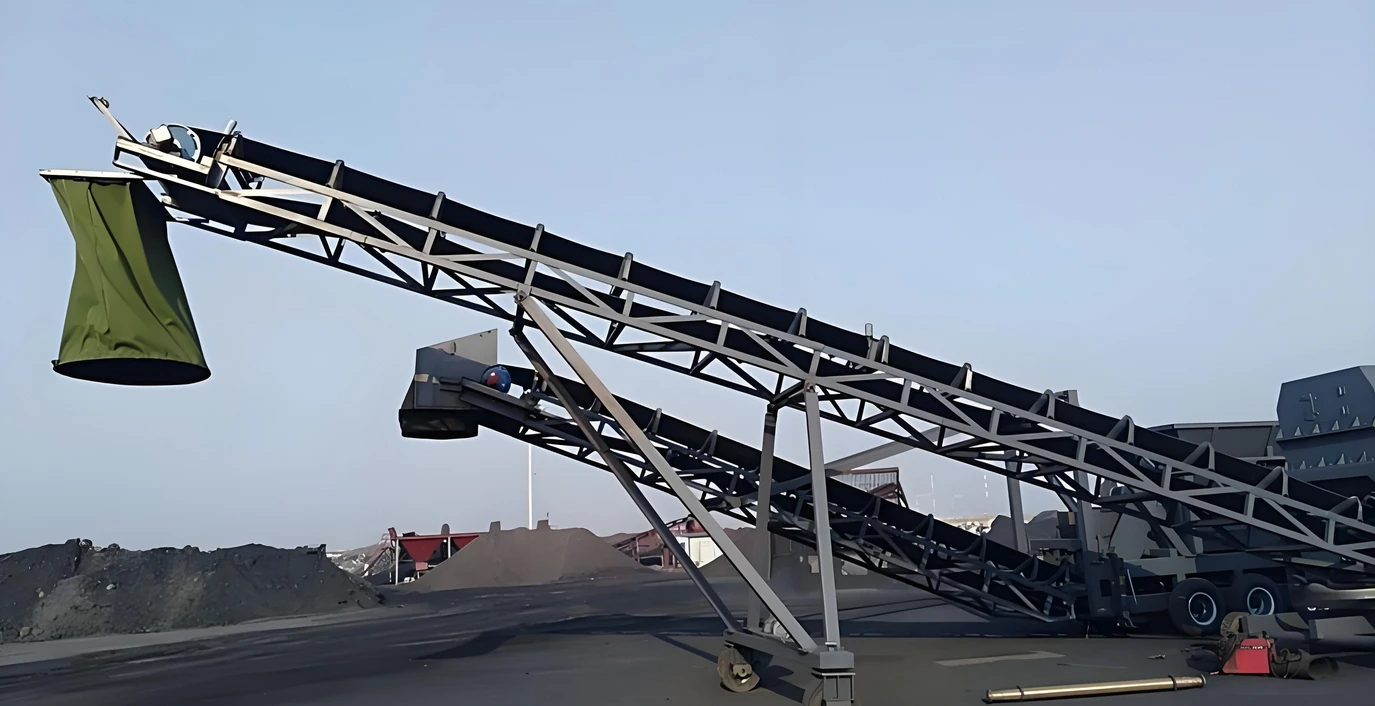
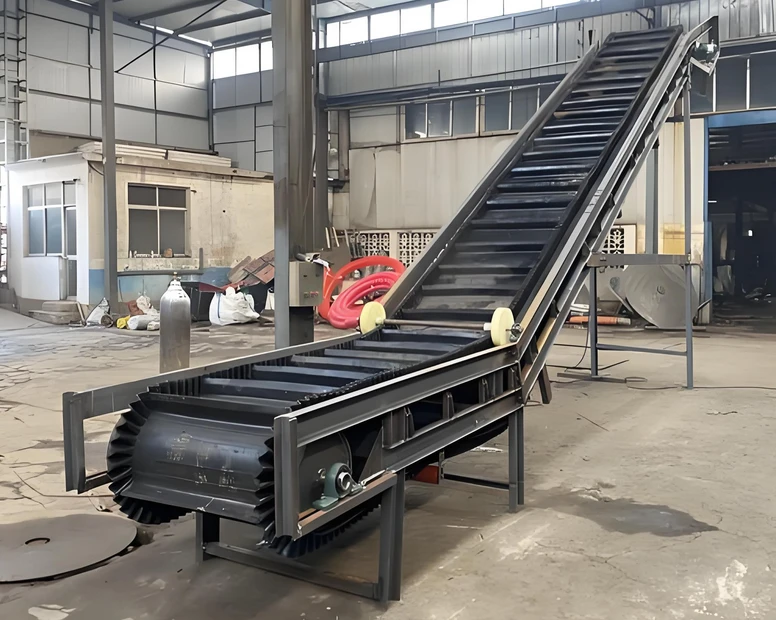
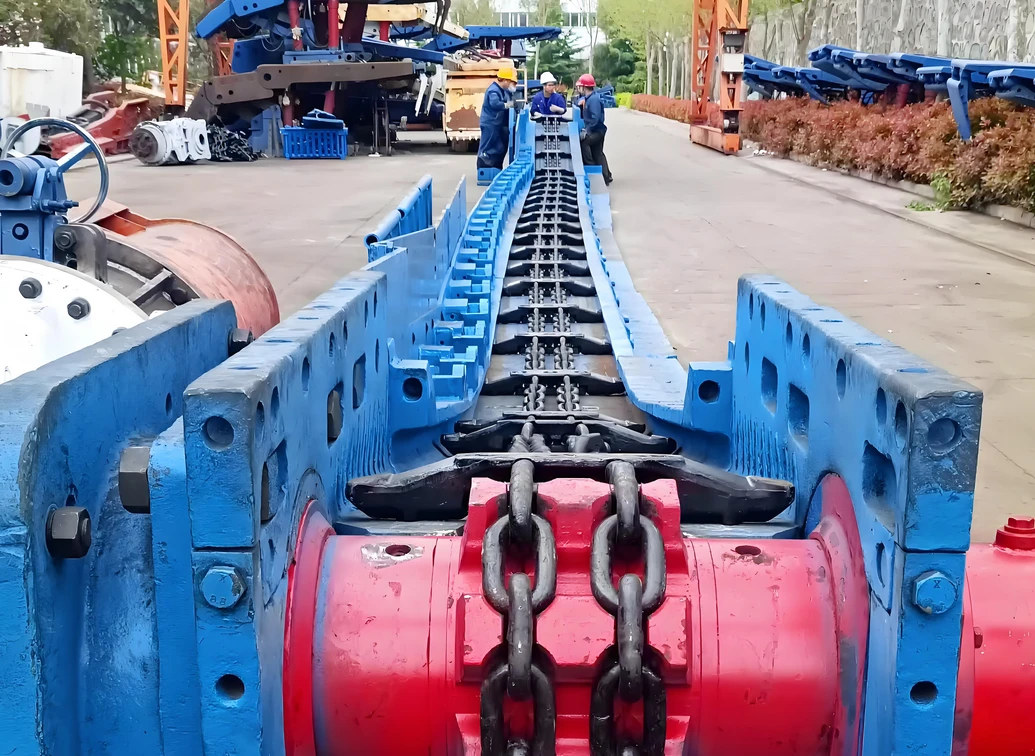
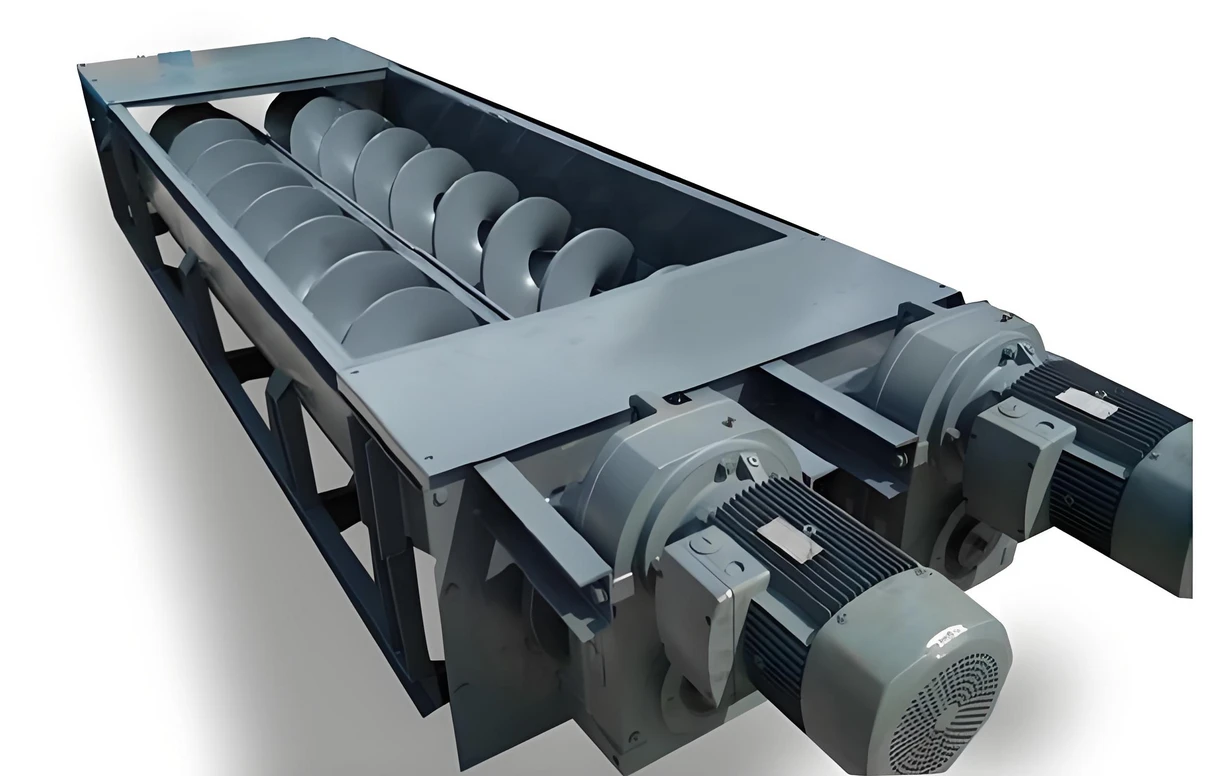
Main components
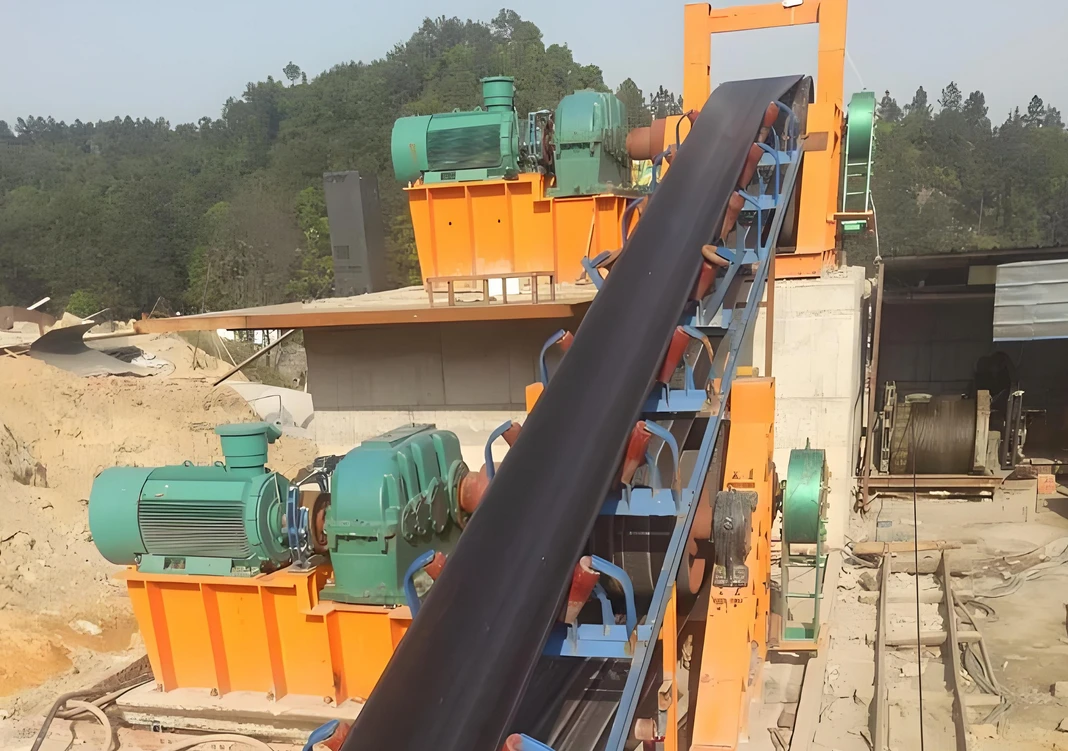
Belt: The part that carries the material, usually made of rubber, PVC or other composite materials.
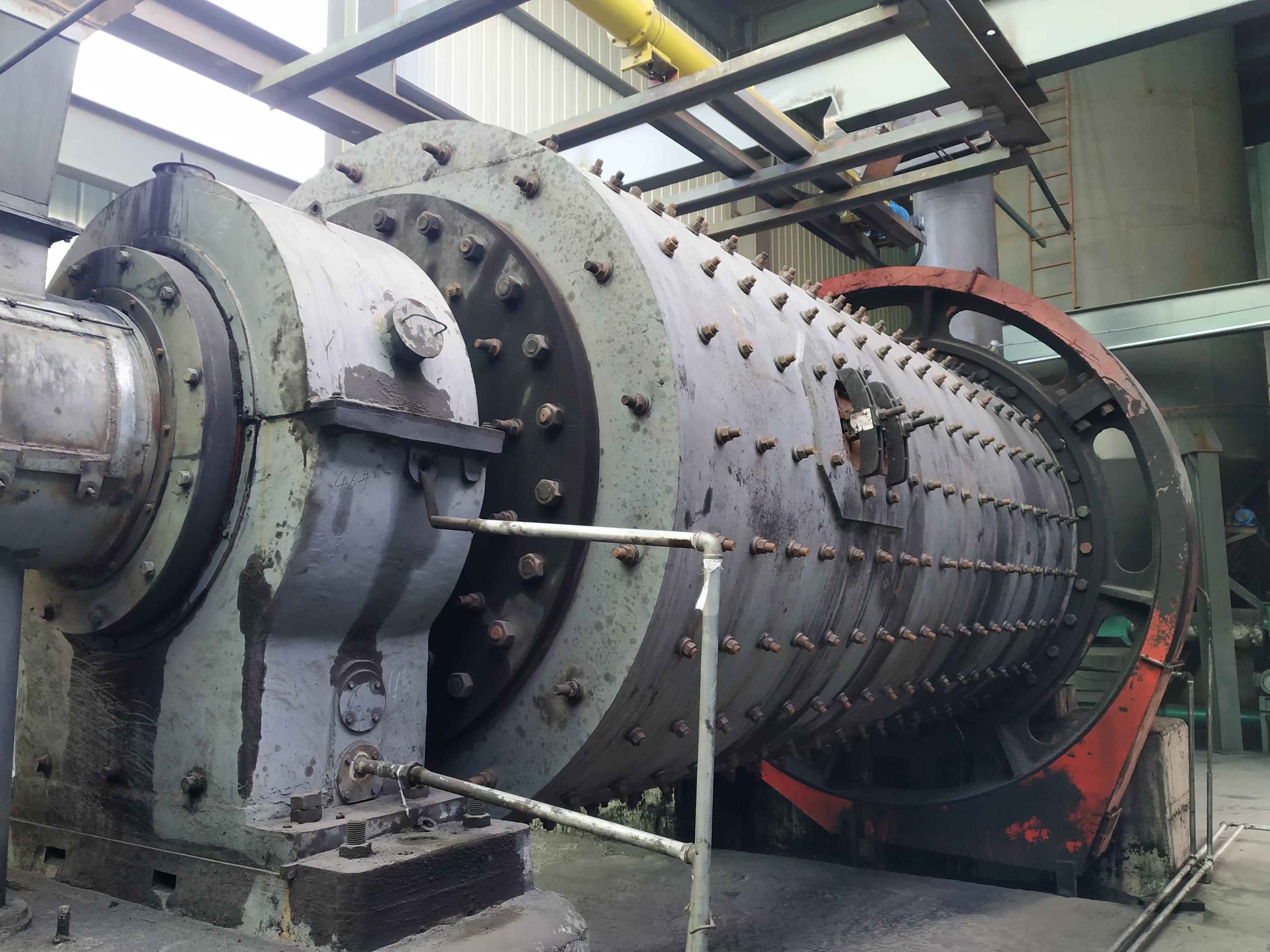
Drive device: It includes motor, reducer and drive roller, which provides power to make the belt run.
Roller: The rolling part that supports the belt and the material, which is divided into load-bearing roller and return roller.
Tensioning device: Maintain the proper tension of the belt to prevent slipping or excessive relaxation.
Frame: The structure that supports the entire conveyor.
Cleaner: Remove the material adhering to the belt to prevent material accumulation.
Protective device: Such as deviation switch, emergency stop switch, etc., to ensure the safe operation of the equipment.
Working principle
The belt conveyor drives the belt to circulate through the drive roller. The material enters the belt from the feed port and is transported to the discharge port as the belt moves. The belt is supported by rollers on the return trip to form a closed circulation system.
Advantages
Efficient: It can continuously transport a large amount of material, suitable for long-distance and large-volume transportation.
Flexible: It can be designed into a horizontal, inclined or curved conveying path as needed.
Low energy consumption: Compared with other conveying methods, it consumes less energy.
Simple maintenance: Simple structure, easy to maintain and operate.
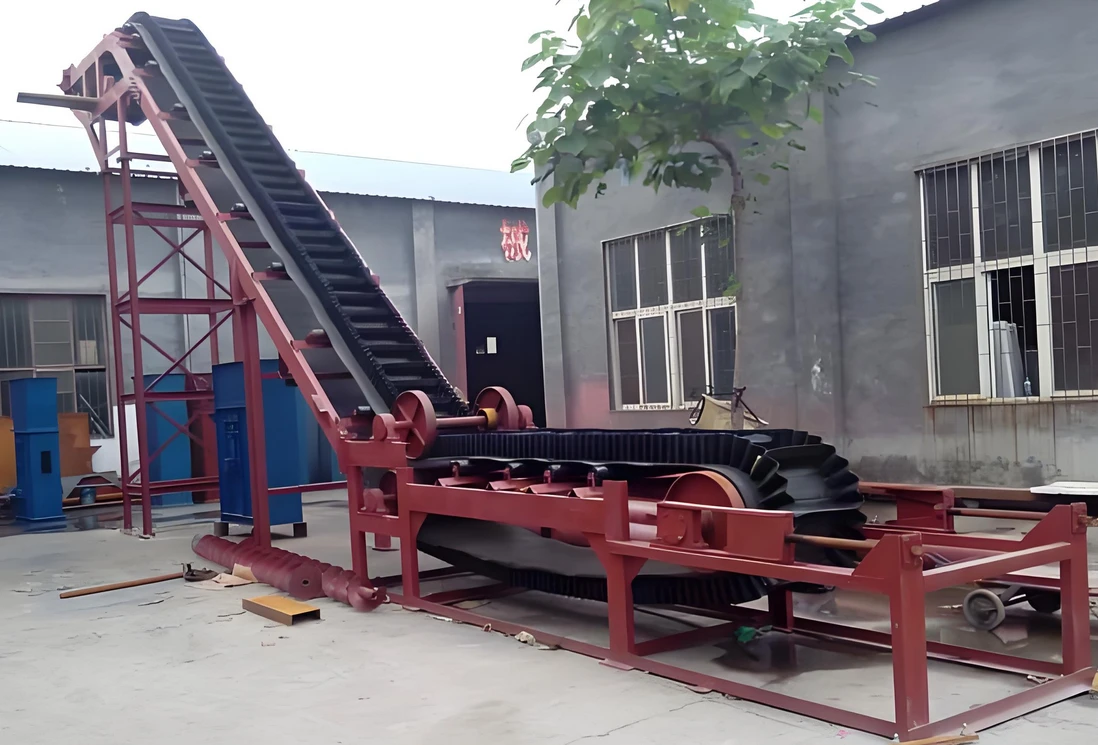

Application scenarios
Mines: used to convey ore, coal, etc.
Ports: used to load and unload bulk cargo.
Factories: used to convey materials on production lines.
Agriculture: used to convey grain and feed.
Common problems and solutions
Belt deviation: adjust the rollers or install a deviation correction device.
Belt slippage: check the tensioning device and increase the tension.
Material spillage: check whether the sweeper is working properly and adjust the feed port position.
Maintenance and maintenance
Regularly check the belt for wear.
Lubricate the rollers and drive device.
Clean the accumulated material on the belt and frame.